
|
Floating-Point Numbers in the Automation Engine |

Knowledge Base |
Agent's Job Messenger |

|
This document serves to introduce the basic terms regarding time in general and time in connection with AE.
Time is made up of a given date and a given time. The indicated time refers to the local time. It is thereby dependent on the pertinent time zone and the use (or non-use) of Daylight Savings Time.
|
Los Angeles (PST) |
New York (EST) |
UTC |
Frankfurt (CEST) |
Tokyo (TYST) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Friday 3rd May, 2002 |
Friday 3rd May, 2002 |
Friday 3rd May, 2002 |
Friday 3rd May, 2002 |
Friday 3rd May, 2002 |
Date
The term "date" always refers to the local date. This date
is therefore dependent on the respective time zone and use (or non-use)
of Daylight Savings Time.
Time
The term "time" always refers to the local time. The time
is therefore dependent on the respective time zone and use (or non-use)
of Daylight Savings Time.
UTC - Coordinated Universal Time
UTC is the international time standard and basis for all time calculations
in AE. UTC is based on the division of the day into 24 hours. Therefore,
afternoon times are specified, for example, as 16:00 UTC (sixteen hours,
zero minutes). There is no daylight savings in UTC. This way the time
and date specification is always precise.
GMT - Greenwich Mean Time
Time
zones are based upon Greenwich Time as the meridian (0º longitude) passes
through Greenwich. Greenwich Mean Time serves as the basis for calculating
time differences to other time zones.
TZ - TimeZone
The areas with time differences to UTC are called time zones. This difference
must not necessarily denote one full hour (60 minutes). The time zones
generally run along the longitudes. Within the political borders of individual
countries, however, the time zones can deviate from the general longitudinal
definition.
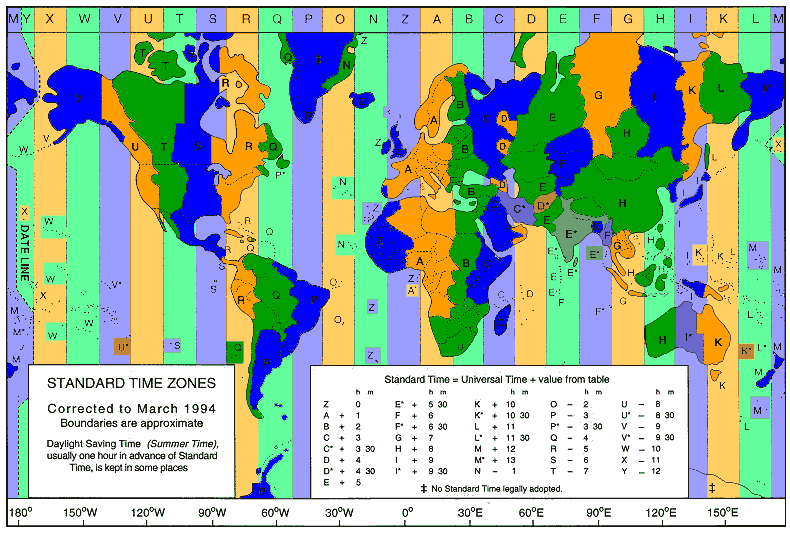
Date Line
The date line lies along the 180° line of longitude.
Standard Time
Standard time is the local time assigned to the pertinent time zone. Standard
time is also occasionally identified as winter time.
DST
- Daylight Savings Time
For daylight savings, the standard time is adjusted forward by a certain
amount of time. Each individual country has its own rules on whether or
not Daylight Savings Time is used, the point in time for the changeover
and the time difference to standard time. Likewise, the chronological
year itself determines if and when daylight savings is implemented. Some
countries are currently in the process of making changes or preparing
to decide upon a Daylight Savings Time arrangement.
The time change from Daylight Savings Time to standard time and vice versa is most commonly 1 hour (60 minutes). Some countries, however, use a difference of more or less than one hour. Furthermore, time change in the northern hemisphere is directly opposite to that in the southern hemisphere. When in the northern hemisphere the changeover to Daylight Saving Time is made, the southern hemisphere simultaneously switches back to standard time. The switch to Daylight Saving Time in the northern hemisphere is made in the springtime, in the southern hemisphere in the fall (autumn).
See also: