Installing AWI with WebLogic
The Automic Web Interface is Automic Automation's graphical user interface. When you download it from our download center, the delivery ZIP file already contains everything that you need to install, start and configure the Automic Web Interface. It also contains the AWI plugins, all necessary bundles and libraries, and the Java API.
It is no longer necessary to install an application server before installing the Automic Web Interface because the delivery artifact includes the AWI Jetty Launcher. However, if you do have an application server (Tomcat, WebSphere or WebLogic), you can still follow the old installation method. This topic provides instructions for installing the Automic Web Interface in all possible setups.
Important: The Automic Web Interface and the AE server must have the same release version. To check other compatibility issues, see Compatibility Information or access the compatibility matrix directly.
This page includes the following:
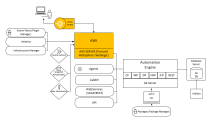
System Overview
The graphic below is a high-level overview of the installation process. The areas where you must do something to install the Automic Web Interface are highlighted.
Click the image to expand it.
AWI and TLS
As of version 21.0, the Automation Engine and the Java components communicate using TLS/SSL. These components establish a connection with the Java communication process (JCP), which uses trusted certificates to prove its identity to other communication partners.
You can use the trustedCertFolder= parameter in the respective configuration file to define the path to the folder where the trusted certificates are stored. Otherwise, the certificates should be installed in the Java trust store. For more information, see Securing Connections to the AE (TLS/SSL).
Content of the Delivery Artifact
The delivery ZIP file that you download from our download center contains the following files and folders:
-
aa-webui-launcher.jar
Launcher to start AWI within a Java process
-
awi.war
Web application file for Tomcat, WebSphere and WebLogic
-
/config
Folder containing the AWI configuration files (
logback.xml,uc4config.xml,configuration.properties, plugin configuration, and so forth)Note: Some configuration files are delivered with an additional ".sample" extension to ensure that your existing configuration files will not be overwritten when you update the AWI installation. You can remove ".sample" and adapt the parameters in these files or you can use the old, already configured files.
-
/lib
EquinoxOSGi runtime libraries
-
/osgi-tmp
Temporary folder for OSGi related files and the AWI log file
-
/plugins/autoinstall
AWI plugins
-
/plugins/java-api-bundles
Java API
-
/plugins/osgi-support-bundles
OSGi runtime (Felix, Service Runtime)
-
/THIRD-PARTY-LICENSES
Folder that contains a copy of the used licenses
-
THIRD-PARTY-LICENSES.txt
List of third-party libraries used in AWI
Prerequisite:WebLogic is already installed. The Automic Web Interface does not require any specific WebLogic configuration.
Overview:
- Deploy the WAR file.
- Configure the connection to the Automation Engine.
- Start AWI
- Configure your Browser.
- Verify that AWI works as expected (health check).
Follow these Instructions:
-
Deploy the WAR file. Refer to the WebLogic official documentation for more information.
-
Configure the connection to the Automation Engine systems.
You have the following options to configure the connections to Automation Engine systems:
-
Using the uc4config.xml configuration file
After launching AWI for the first time, the uc4config.xml.sample file is created in the awi\config folder in your installation path. You can rename it (remove the additional .sample extension) or you can copy an old, already configured file to this folder.
The uc4config.xml file lets you define connections to more than one AE system.
If you define multiple connections, you must configure the automationEngine.index property of the configuration.properties file. In this property you define whether users will be able to select between those connections or whether they will be able to connect only to the first connection specified in uc4config.xml.
For the changes to take effect, stop and restart the application server.
-
Using environment variables
When you configure a connection to the Automic Web Interface using environment variables, the following applies:
-
When you log into AWI, this connection is displayed in the Connection field and in its drop-down selection list.
-
The uc4config.xml file is no longer required.
However, you can use both environment variables and uc4config.xml. If the connection and system names used in the uc4config.xml file and in the environment variable are the same, the environment connection is used. If the names are different, both connections are listed and selectable in the Connection field.
-
You can define only one Automation Engine connection.
If you want to define more that one, set the automationEngine.index property in the configuration.properties file to something other than -1. As a result, the AE connection defined in the environment variable is ignored and is not displayed in the Connection field.
- If you use an environment variable to define a trace level, this value also overrides the one defined in the uc4config.xml file. Otherwise, the default value is used.
Environment Variables for AE Connections
All environment variables for AE connections must use the prefix AUTOMIC followed by an underscore: AUTOMIC_.
Environment variables for AE connections Key Description AUTOMIC_SYSTEM_NAME (Mandatory) Name of the Automation Engine system you want to connect to.
When logging into AWI, in the Connection field and in its drop-down selection list, the system name is displayed in parenthesis next to the connection name.
Example:
- AUTOMIC_SYSTEM_NAME: AUTOMIC
- AUTOMIC_CONNECTION_NAME: AE_TEST
- Connection: AE_TEST (AUTOMIC)
AUTOMIC_CONNECTION_NAME (Optional) Name of the connection.
If this value is not defined, the system name is used also as the connection name.
Example:
- AUTOMIC_SYSTEM_NAME: AUTOMIC
- AUTOMIC_CONNECTION_NAME:
- Connection: AUTOMIC (AUTOMIC)
AUTOMIC_SYSTEM_CPS (Mandatory) Description: Definition of the connection to the communication processes (JCPs) of the Automation Engine system
Value: Address (IP address:Port) or (hostname:Port) of the JCPs, separated by a semicolon
Example:
127.0.0.1:2217;127.0.0.1:2218
AUTOMIC_TRACE_LEVEL (Optional) Description: Trace level of XML operations
Allowed values: 0 - 3
- 0: off
- 1: send calls
- 2: receive calls
- 3: all
Environment Variables for General AWI Properties
You can also use environment variables to define custom property settings for the communication between the Automation Engine and the Automic Web Interface. You must use the prefix AUTOMIC followed by an underscore for these variables, too.
Key:AUTOMIC_<Property name> (all uppercase)
Value: Property value
Example:
AUTOMIC_AUTOMATIONENGINEOPENCONNECTIONTIMEOUTMILLISECONDS=9999
Also, if the property name includes a period, you must replace the period with an underscore. For example, the property name for automationEngine.index must be defined as AUTOMIC_AUTOMATIONENGINE_INDEX.
-
-
-
-
Enter http://hostName:<port>/AWI/ in the address bar of your Internet browser:
-
hostName = The name of the computer on which the application server runs, such as "localhost".
-
<port>= The default port for the application server, which may vary depending on the setup of the application server.
-
-
Log in to Client 0 with your user name and password.
Client 0 is a system Client that is supplied by default with your installation. Here you add further Clients, create Users, assign them to their corresponding Clients, and so on. For more information, see System Client 0000 .
-
-
- Enable cookies
- Disable pop-up blockers
- Empty the cache after each upgrade
-
Verify that AWI is working as expected (health check).
Use the AWI's health check to verify that the application server has deployed AWI correctly and that it is up and running.
-
Add the word status to the URL:
http://hostName:<port>/AWI/status
-
The standard HTTP 200 OK status response code is returned and a page is displayed with the word OK indicating that AWI is running. Otherwise, the corresponding standard HTTP message is displayed.
You can use this health check endpoint in your internal URL monitoring systems to ensure that AWI is functioning properly.
You can also use this endpoint in Shell scripts to call the status of the Automic Web Interface.
-
See also:
AWI is running successfully. Now you can start configuring it. The following topics guide you through the AWI configuration activities:
-
Configuring the Automic Web Interface
This topic provides the following information:
- Optimizing the server configuration sizes
- Securing access via TLS
- Customizing the configuration path
- Configuring the log in and user authentication
- Configuring the logging
- Customizing the user interface
- Setting up the load balancer and configuring proxies
-
uc4config.xml - Configuring the Connection Between AWI and AE
This topic describes how to define the connection to the Automation Engine system
-
configuration.properties - Configuring Your Local Setup
This topic describes how to define how the communication between the Automation Engine and the AWI server, and AWI and its clients runs
-
logback.xml - Configuring Log Levels
This topic explains how the AWI handles logging
-
colors.properties - Configuring the Color Scheme
This topic explains how to configure the AWI color scheme
See Troubleshooting Problems on AWI Clients for tips about how to ensure that users see all AWI parts correctly and have no login problems.
After installing and configuring AWI you can start setting up your system or you can continue with the installation of other plug-ins and components.
For more information, see Requirements and Installation Types.
See also Installing the Automic Web Interface.