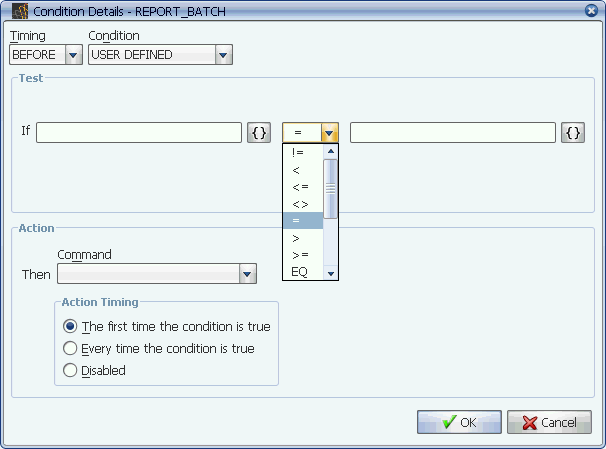
Select a qualifier from the drop-down box.
Qualifier values are available based on the condition you select. You can pick from string and numeric qualifiers.
Qualifiers are used to evaluate two values in the Test box fields of a condition as shown below. The condition you select determines the qualifiers that are available from the drop-down box.

Select a qualifier from the drop-down box.
Qualifier Types
The qualifier you select determines the way the condition is evaluated. The two types of qualifiers are:
| Qualifier type | Evaluates the condition values as: |
|---|---|
|
String |
A left to right sequence of characters. |
|
Numeric |
Mathematical statements. |
If you select the wrong type of qualifier, Applications Manager may not evaluate your condition the way you intend it to. For example, Applications Manager evaluates '1000 GT 50' as true (because one thousand is more than fifty), and '1000 > 50' as false (because 1 does not come after 5 alphabetically).
Qualifier Descriptions
Qualifier descriptions are listed in the table below.
| Qualifier | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
!= or <> |
String |
Not equal—both signs evaluate the same. |
|
< |
String |
Less than. |
|
<= |
String |
Less than or equal to. |
|
= |
String |
Equal to. |
|
> |
String |
Greater than. |
|
>= |
String |
Greater than or equal to. |
|
LK |
String |
Is like-uses a substring search to check if the second value occurs in the first. You might use this qualifier to determine whether a substring exists in a dynamic substitution variable's value. |
|
GE |
Numeric |
Greater than or equal to. |
|
LE |
Numeric |
Less than or equal to. |
|
GT |
Numeric |
Greater than. |
|
LT |
Numeric |
Less than. |
|
NE |
Numeric |
Not equal. |
|
EQ |
Numeric |
Equal to. |
Substitution Variables Evaluated as Characters or Numbers
Applications Manager evaluates substitution variables as characters or numbers depending on the qualifier value used in the Condition Details window. For example, the condition #flow = bad will be evaluated as a string. The condition #count_employees LE 100 will be evaluated numerically.
To ensure proper evaluation of dates, use YYYYMMDD format with string qualifiers (>, <=, =) or Julian dates (dates expressed as the number of days elapsed since January 1, 4713 B.C.) with numeric qualifiers (for example GE, LE).