What's New in 24.2.0
This section provides information about the new features and enhancements that have been implemented in version 24.2.0.
This page includes the following:
Automic SaaS
Automic SaaS and Automic Automation versions have slightly different release cadences. This is why you may read about features in the product documentation that are not available on your environment yet. This deviation in content happens only during a short period of time.
In addition to the other new Automic Automation features described in this topic, Automic SaaS has been enhanced as follows:
-
You no longer need to place a service request for the following:
-
Creating Clients
-
Creating Users
-
Importing object definitions
-
-
So far, restrictions due to the database access prevented you from using SQLI and SEC_SQLI VARA objects, since they retrieve values from the database through SQL statements. From this version onward, using these VARA objects is also possible in Automic SaaS environments. For more information about these objects, see SQLI VARA Objects and SEC_SQLI VARA Objects.
-
Moving object and data definitions from Automic Automation on-premises to Automic SaaS is easier thanks to the improvements made to the Transport Case. For more information, see Enhanced Importing/Exporting/Transport Case Functionality in AWI.
See also the information about the enhancements to the AE REST API.
New Automic Automation Help
So far Automic Automation provided context-sensitive help in the way you know it from many other applications: By clicking on the Help button, a topic explaining the AWI area where you were opened up on a new browser tab. As of this version, when you click on the Help button, the Automic Automation Help opens in a panel within AWI and not in a new browser window. This panel gives you access not only to the Automic Automation product documentation, but to much more content: Knowledge Base articles, community posts, Education content, and so forth. For more information see Using the Documentation.
General Enhancements
This version introduces the following new features:
Dedicated Database User for SQLI and SEC_SQLI VARA Objects
Automic Automation 24.2.0 introduces an additional security layer on your database administration. Now, your database administrator has the ability to restrict the definition of the database user to just have read-only rights to the database. This user can be used when executing SQLI or SEC_SQLI objects. By preventing the database user from being able to write or delete records from the database, you make sure that the database remains intact when users access it through SQLI or SEC SQLI VARA objects.
To add this security feature to your system, you must configure the following objects:
-
A new key in the UC_SYSTEM_SETTINGS variable called SQLI_LOGIN.
-
A Login (LOGIN) object of type DB that contains the credentials (user name and password) for the database user.
For information about how to set up this function, see Securing the Database.
New Authentication Method: User Tokens (aka Bearer Tokens)
So far, the only supported authentication method behind a User login was Basic Authentication; the only for users to log in to Automic Automation was through their user name and password. As of 24.2.0, a new additional authentication method is available both in AWI and through the REST API, the JavaAPI and the CallAPI, namely, User Tokens (also known as bearer tokens).
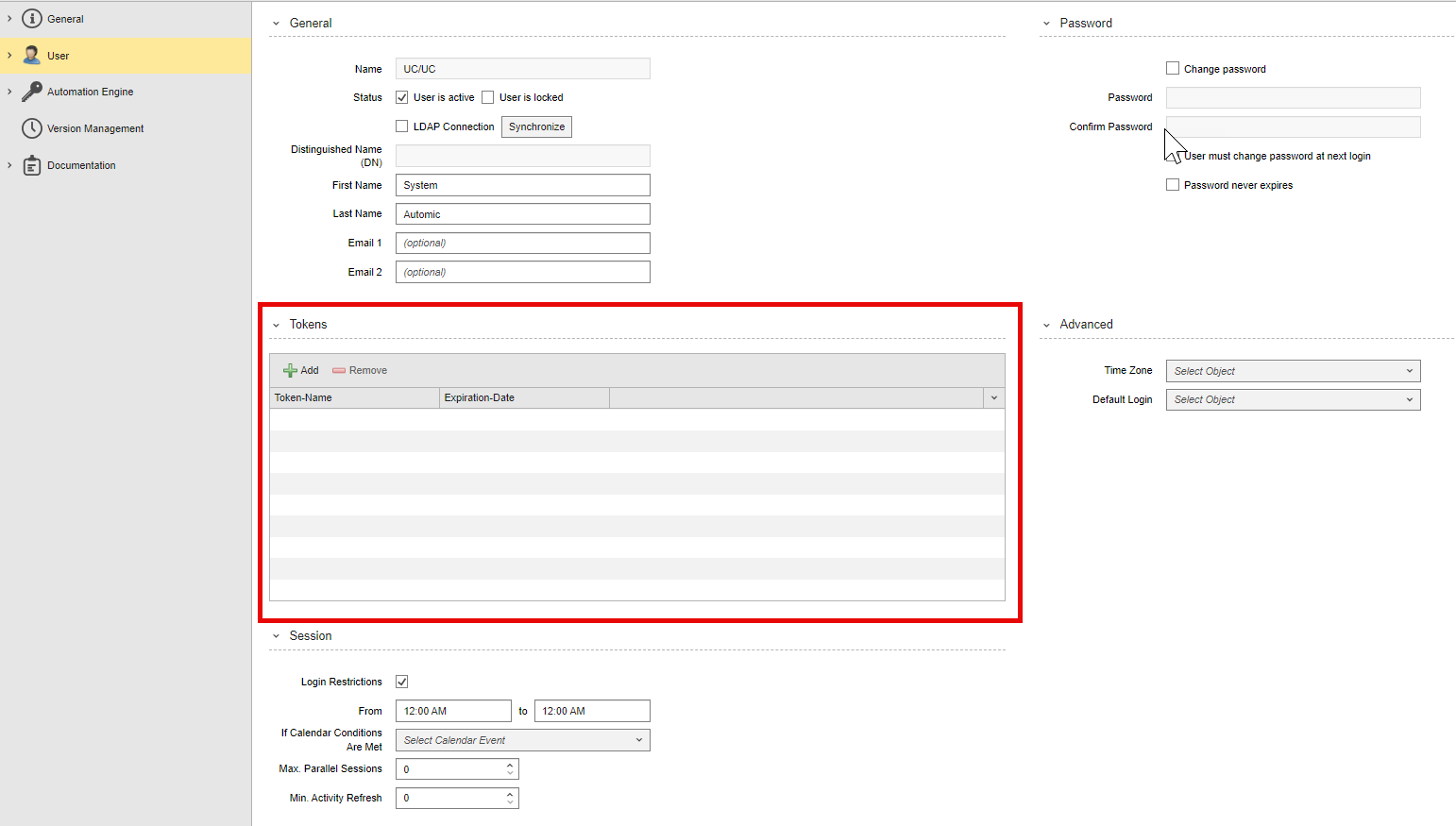
With this version, users with the necessary privileges can generate and manage their own tokens. In AWI, a new section is now available in the User object definition that lets you generate and manage user tokens:
(Click to expand)
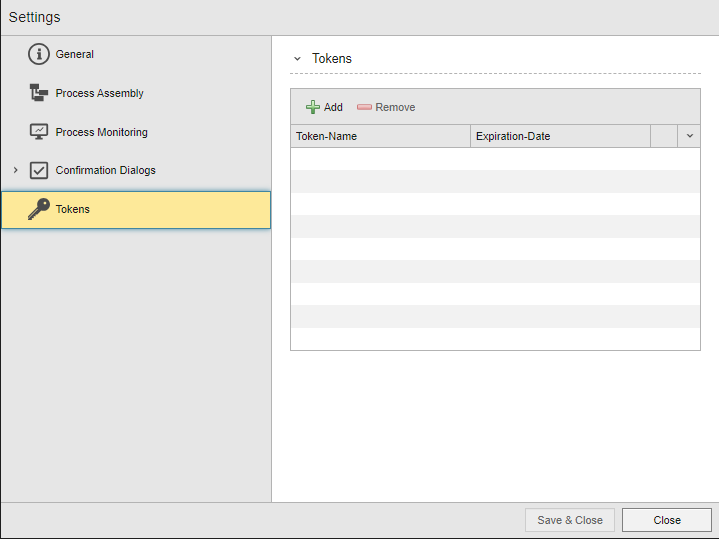
Users who do not have access rights to their User object definitions can generate and manage their tokens in a new tab called Tokens on the User Settings dialog:
(Click to expand)
New Privilege
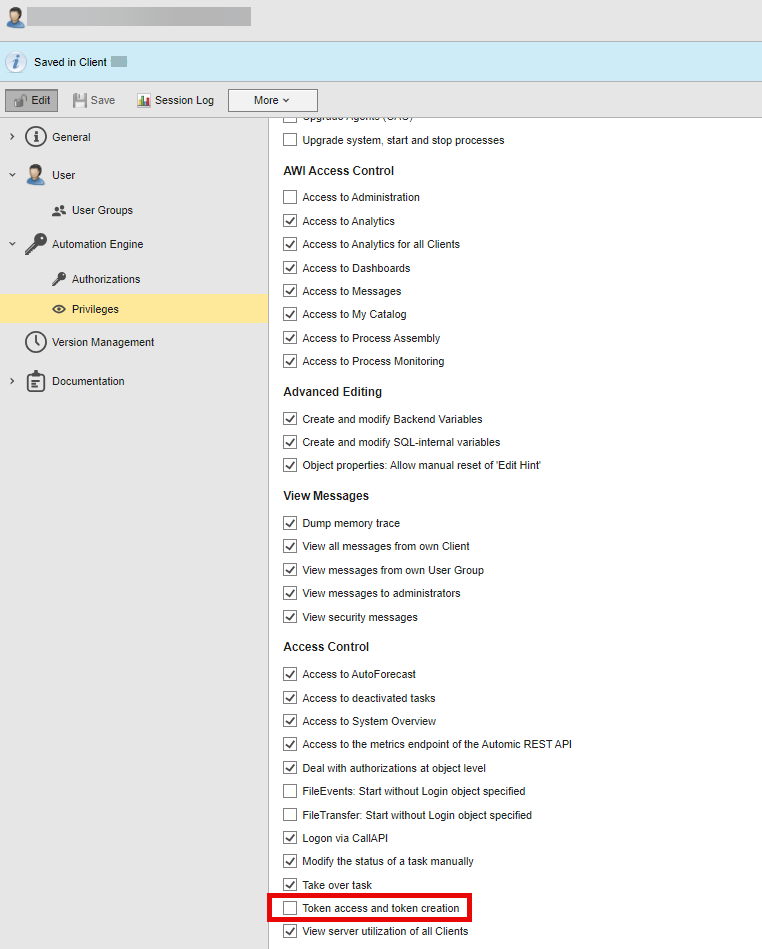
A new privilege called Token access and token creation has been introduced to enhance the security of this new function. Only users with this privilege can generate and manage their tokens:
(Click to expand)
New System-Wide Variable
User tokens have an expiration date. A new system-wide variable lets you restrict the maximum validity period that Users can define when generating their tokens.
For more information, see:
Important!
A token is always tied to a User object. However, bad practices when storing and/or using them can lead to accidentally exposing them publicly. It is recommended that you enforce a strong security policy to avoid these situations. These recommendations can help you with it:
-
Protect the token by separating your REST client from the location where you store the token,
-
Delete tokens that are no longer needed.
-
Rotate the tokens periodically and define expiration times that are no longer than necessary and that they comply with your company's security policy.
Enhanced Importing/Exporting/Transport Case Functionality in AWI
In previous versions, to transfer large amounts of object definitions from one Client to another, or from one Automation Engine system to another, you used the Transport Case feature in combination with three Utilities: AE DB Unload, AE DB Load and AE DB Change. This method requires access to the AE database.
Version 24.2.0 introduces enhancements to the Transport Case and import functions to help you transfer data among instances without having to use any AE DB utility, that is, without having to access the AE database. This new feature is particularly useful if you want to transition from Automic Automation on-premises to Automic SaaS, since you will not be able to access the target (that is, the Automic SaaS) database. As of this version, after moving your object definitions to the Transport Case, you can export the content of the Transport Case to a data.txt file that is saved to your Downloads folder by default. You can then import the file into the target system (for example, your Automic SaaS instance) directly from AWI though the regular Import function or using the REST API.
A new system-wide variable called MAX_TC_SIZE determines the maximum size allowed for the data.txt file, no matter whether you import/export it directly from AWI or through the REST API.
For more information, see
Automic Web Interface
Accessibility Enhancements
BROADCOM is committed to continuously improve the accessibility of its products. In this respect, AWI has been enhanced as follows:
-
Most of the labels contain now descriptions to support screen readers.
-
Heading markup has been added where missing
-
Table markup has also been added to most lists
-
Alternate texts have been added where missing. Existing alternate texts have been improved.
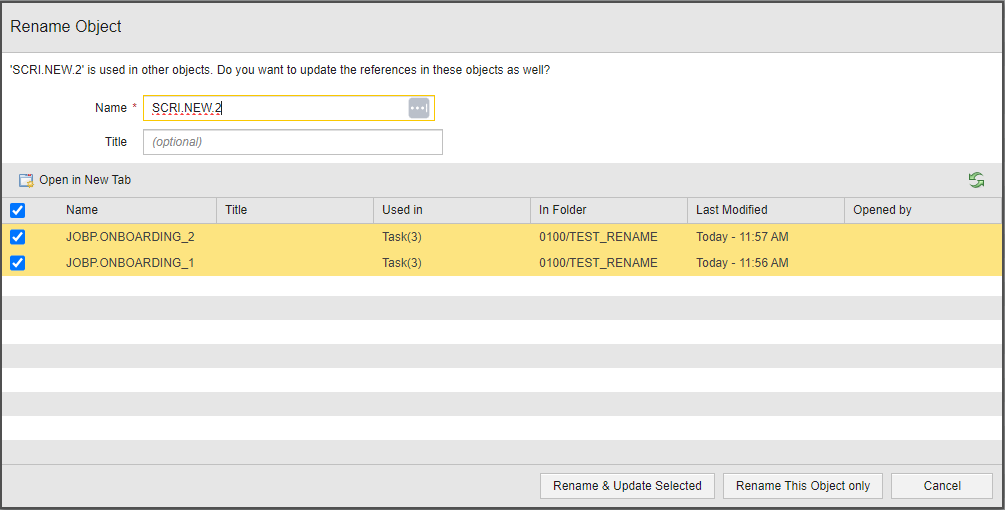
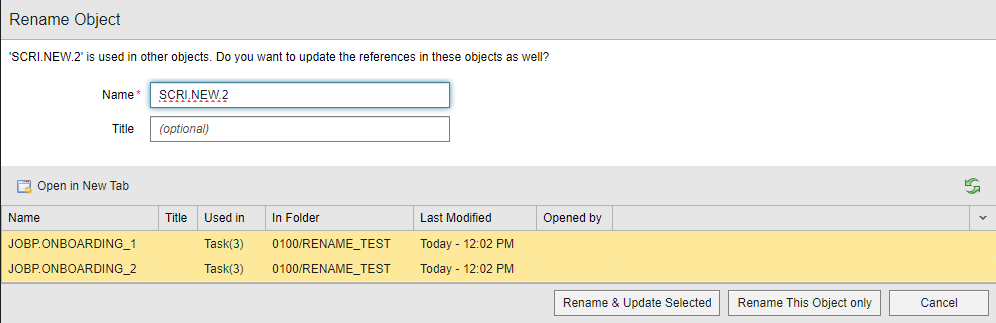
Improved Rename Objects Dialog
The Rename Object dialog has changed slightly. So far, it contained checkboxes before the object names that you had to activate/deactivate to perform the name change on the corresponding objects. This is what the dialog looked like until now:
(Click to expand)
The checkboxes have been removed now. To select/deselect object in the list, you simply click on them. The yellow background indicates which objects are currently selected:
(Click to expand)
Other than that, the behavior of the dialog remains the same. For more information, see Renaming Objects and Folders.
AE REST API
This version introduces numerous enhancements to the AE REST API.
Defining and Reading Authorizations at Object Level
As of this version you can both define (add or revoke) and read authorizations at object level when creating or editing an object by using POST, PATCH and GET. Automic Automation tracks the User logins for both forbidden and authorized access provided LOGON ( SECURITY Parameters and object auditing (OBJECT_AUDIT) are enabled.
Granting Privileges and Authorizations to Users and User Groups
You can now use the REST API to specify which privileges and authorizations Users and User Groups should have. In the case of privileges, the REST API nomenclature is slightly different to the labels used in AWI. See Granting Automation Engine Privileges for a detailed description of the AE privileges that provides the names of the privileges both in AWI and in the REST API.
Note: The only notable difference between the authorizations in AWI and in the REST API is that in AWI you select the NOT group to deny rights; in the REST API you must use 0 (null) in your REST request. See Granting Automation Engine Authorizations.
Enhanced REST Request Log
With version 24.2.0, the REST request log is enhanced to provide information about the user and connection that performed the request. This information can look like this:
U00045098 Method 'GET', URL: 'http://XXXXXX:8088/ae/api/v1/100/system/features', received from IP: 'xx.yy.zz.abc' from user 'SMI/DEV'
User Login Tracking
In the SECURITY Parameters client variable administrators define the security audit logs for authorized and/or denied accesses in the categories login, privilege, host access and object access. As of v24.2, if the LOGON parameter is enabled, User logins through the REST API are tracked for both forbidden and authorized access. For more information, see SECURITY Parameters.
Exporting/Importing Transport Case Files
The AE REST API has been enhanced to support exporting and importing Transport Case files.
Granting Authorization and Privileges
You can use the AE REST API to grant or deny AE authorizations and privileges for User and/or User Groups. You can also grant authorizations at object level.
For more information, see AE REST API - Granting Authorizations and Privileges.
Generating and Managing User Tokens
See New Authentication Method: User Tokens (aka Bearer Tokens).
New REST API Endpoints
This version includes the following new AE REST API endpoints:
-
Disconnect Agent Groups
-
Get the ZDU status
-
Perform an action in the ZDU process (begin, check db, upgrade and so on)
These are available for a Zero Downtime Upgrade for versions 24.0 and higher.
For more information, see REST API Reference.
Automic Automation Kubernetes Edition
This version introduces the following new features in AAKE:
Enabling and Disabling Analytics
So far, when deploying AAKE you had to decide right from the beginning whether you wanted to deploy Analytics too and you couldn't change this configuration later on.
As of this version, when you deploy AAKE, you can decide whether you want to also deploy Analytics so that it also runs in your cluster or not. If you do not deploy it at the beginning you can still decide to install it later. Likewise, if you decide to deploy it at the beginning and want to disable it later on, you can also do so. You enable/disable Analytics by specifying true/false in the corresponding section of the values.yaml file. For more information, see Preparing for the Container-Based Installation.
Horizontal Pod Autoscaling
This version of AAKE introduces horizontal pod autoscaling allowing you to automatically update your workload resources to match your system's demands.
In the values.yaml file, you can define if you want to use autoscaling or not and define other parameters such as CPU and memory utilization or the minimum and maximum number of replicas.
For more information, see Scaling Deployments
New and Changed Persistent Volumes (PV) and Persistent Volume Claims (PVC)
As of this version of AAKE, the PVC configuration for logging and tracing in the values.yaml file is split. That means that you can configure one PVC for logging and a separate one for traces.
Also, as of this version, you can store the following elements on a Persistent Volume (PV):
-
Lucene index cache
-
Certificate management folder
-
Analytics security folder
As with the logs and traces, you can define the PVC configuration for these new PVs in the values.yaml file.
For more information, see Configuring your Automic Automation System before Deployment.
Automatic Restart of AE and Analytics Pods
As of this version, the different AE processes and/or Analytics pods are restarted automatically upon modifying the AE or Analytics database secrets, for example, when updating the database passwords.
AAKE Install Operator
As of this version, the Install Operator is built with OpenJDK 17 LTS.
Agents
This version introduces the following:
Java Based Linux PowerPC 64 LE Agent
This version introduces the Java based Linux PowerPC 64 Little Endian Agent. It allows you to send secure emails and use UTF-8 characters.
The Agent requires a JRE (version 11 or higher) on every machine in which an Agent is running; therefore you have to make sure JRE is available. It also requires the latest version of the Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable Package.
Note: The Linux PowerPC 64 Big Endian Java based Agent will be released with future v24 updates.
For more information, see:
Cloud Integrations
Automic Automation has many cloud integrations available on Broadcom's https://marketplace.automic.com/. The following cloud integration Agents have been released or enhanced since Automic Automation's last release:
-
GCP Dataflow, see Automic Automation / GCP Dataflow Agent Integration
-
Email Agent, see Automic Automation / Email Integration
For more information on cloud integrations, see Cloud Integrations.
See also: