Working with Artifacts
As an Application Developer, you use Artifacts to identify and re-deploy the exact same version of a Component deployment on a different Environment.
Important! The actions that you can perform depend on your folder permissions, see: Folder Permissions.
This page includes the following:
About Artifacts
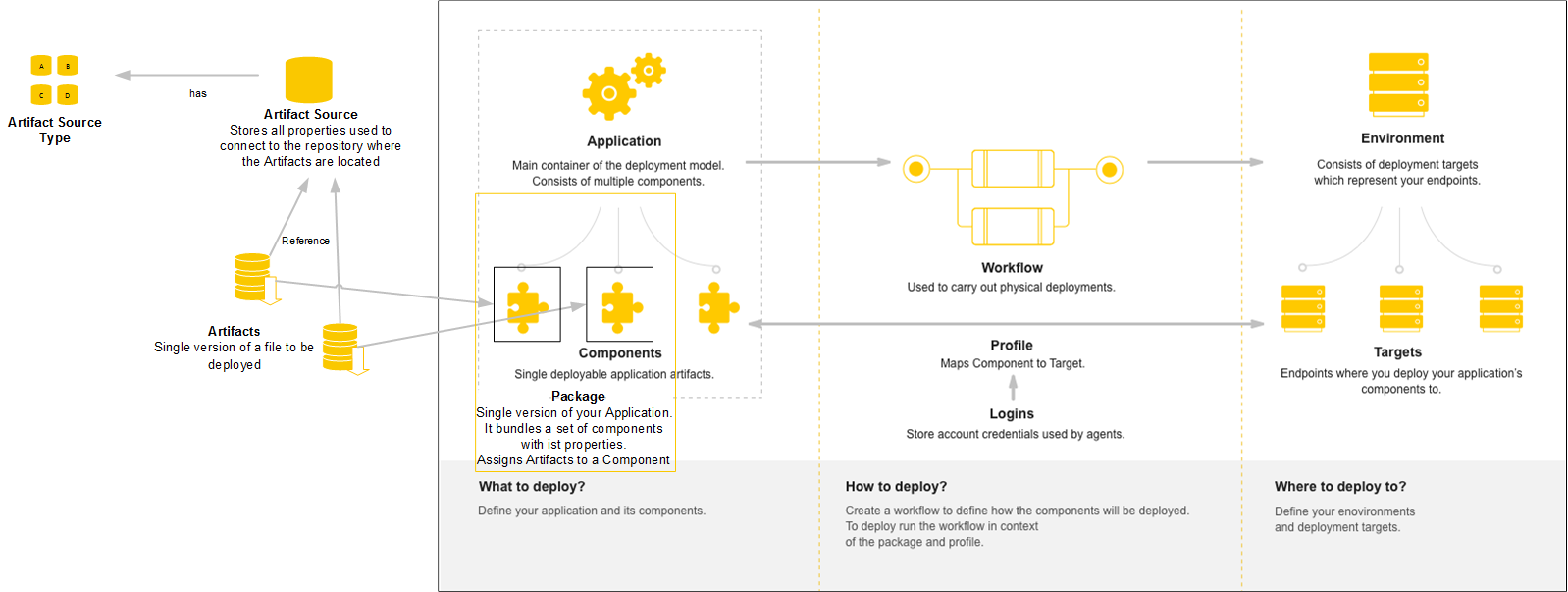
Artifacts are single versions of Application Component deployments, which are located in a certain repository. Artifacts may contain different types of files. To access each repository type, connection properties must be defined at Artifact Source Custom Type level. Artifacts reference real files in the repository, which contain the Component version. Examples of Artifacts are: MyApp_05.02.2018.jar, DB-??.sql, /db/v3/scripts/*.sql, MyRepo LATEST.
An Artifact is a version of a file to be deployed. In a Package, an Artifact is created for each Component.
Click the image to expand it.
Artifact Sources store all properties that are used to connect to the repository where the Artifacts are located. The type of data that is stored depends on the Artifact Source type (for example, URI, user, password). You can define an unlimited number of Artifact Sources in the system.
Artifact Source custom types (for example, HTTP or FPT) can be either manually defined or installed via Action Packs.
Prerequisites
Note the following before working with Artifacts and Artifact Sources:
-
CDA Artifacts are only compatible with the following Action Pack versions:
- PCK.AUTOMIC_BOND 1.2.0 or higher
- PCK.AUTOMIC_ARTIFACTORY 1.2.0 or higher
- PCK.AUTOMIC_FTP 1.2.0 or higher
- PCK.AUTOMIC_HTTP 1.2.0 or higher
- PCK.AUTOMIC_JBDC 1.3.0 or higher
- PCK.AUTOMIC_SMB 1.2.0 or higher
- PCK.AUTOMIC_Tomcat 1.2.0 or higher
- PCK.AUTOMIC_NEXUS 1.2.0 or higher
- PCK.AUTOMIC_NEXUS_V3 1.1.0 or higher
- PCK.AUTOMIC_GIT 1.1.0 or higher
Note: Changing the Properties of an Artifact - If both the Git Branch Name and Git Commit fields are filled in, the Git Commit property is applied.
- PCK.AUTOMIC_SCP 1.2.0 or higher
- PCK.AUTOMIC_SVN 1.2.0 or higher
- PCK.AUTOMIC_TFS 1.3.0 or higher
For more information, see compatibility matrix.
-
PCK.AUTOMIC_BOND must be installed/upgraded first. See: Troubleshooting Installation and Upgrade Errors
Recommended Design Sequence
Your Artifact Model should be designed in the following order:
- Define the Artifact Source. You may need to create a new Custom Type for the new Artifact Source first.
- Create an Artifact.
- Create a new Package or assign the Component to an existing Package.
- Assign the Artifact to a Component. (See: Assigning Artifacts to Components)
- Assign the Artifact to a Package Component. (See: Creating and Assigning Artifacts to Package Components)
Viewing Artifacts
Tip: For more information about how to search for entities and narrow down the results, see: Global Search
- Open the Release Automation perspective.
- Click the Applications tab.
- Double-click a Component to open it.
- Click the Artifacts tab. The list of Artifacts that are defined for the current Component is displayed.
Note: Click the nested tree to display the content of an artifact directory.
Note: Alternatively, you can view the Artifacts related to a specific Artifact Source from the Artifacts view. See: Working with Artifact Sources
Viewing Artifact Files
- Open the Release Automation perspective.
- Click the Applications tab.
- Double-click a Component to open it.
- Click the Artifacts tab. The list of Artifacts that are defined for the current Component is displayed.
- Click an Artifact to see its Artifact files.
Note: The artifact file metadata are displayed in the Properties view of an Artifact file. CDA uses checksums to retrieve the correct artifact content to be deployed.
Viewing Installations of an Artifact
See: Application Installations
Viewing Artifact Assignments
The Package Assignments view shows all Components to which the Artifacts have been assigned.
Artifact Statuses
Artifacts can have one of the following statuses:
- Ready: All Artifact files have been uploaded and are ready for deployment.
- Transferring: There are still files waiting to be uploaded (the complete flag has not been checked by the user)
- Invalid: At least one Artifact file has not been successfully uploaded.
Important! Artifacts with status "Invalid" cannot be assigned to Components or Packages.
- Unavailable: The artifact has been previously used and is referenced by other entities (for example: a Package), but has been removed from the system in compliance with the cleanup rules. For more information, see: DB Cleanup Configuration
Artifact files can have one of the following statuses:
- Transferring
- Transfer Failed
- Ready
- Deleting
- Deleting Failed
- Uploading Failed
Creating Artifacts
Artifacts can be created:
-
From an Application Component:
- Open the Release Automation perspective.
- Click the Applications tab.
- Double-click an Application to open it and select a Component.
- Click the Artifacts tab at the top of the view.
- Click the Create Artifact button in the toolbar. The Create Artifact dialog is displayed.
- Select an Artifact Source.
- Enter a name for the new Artifact.
- The Source Path and Archive Type (for example .zip, .tar, .tar.gz) fields are populated with the values defined in the Artifact Source custom type. Both fields are editable.
Note: If the Archive Type is not empty, the system will unpack the content of the Artifact while transferring the Artifact to the Target.
- Select the folder where you want to store your Artifact.
- Enter the remote artifact checksum file to be downloaded (See: GetArtifact Action in Component Workflows).
Notes:
- The supported checksum types are .md5 and .sha1
- The checksum file name and the source file must be the same. For example:
Source Path: \shared\jpetstore\Jpetstore.zip
Checksum path: \shared\jpetstore\Jpetstore.zip.md5
- Click Create.
-
From the Artifacts list of an Artifact Source:
- Open the Release Automation perspective.
- Click the Artifact Sources tab.
- Double-click an Artifact Source to open it.
- Click the Create Artifact button in the toolbar. The Create Artifact dialog is displayed.
- Enter a name for the new Artifact.
- The Source Path and Archive Type (for example .zip, .tar, .tar.gz) fields are populated with the values defined in the custom type. Both fields are editable.
Note: If the Archive Type is not empty, the system will unpack the content of the Artifact while transferring the Artifact to the Target.
- Select the folder where you want to store your Artifact.
- Enter the remote artifact checksum file to be downloaded (See: GetArtifact Action in Component Workflows).
- Click Create.
-
From the Components list of a Package.
- Open the Release Automation perspective.
- Click the Packages tab.
- Select the Components tab.
- Select a Component.
- Click the + inline button next to the Component name to create and assign the Artifact.
- In the dialog, select an Artifact Source.
- Enter a name for the new Artifact.
- The Source Path and Archive Type (for example, .zip, .tar, .tar.gz) fields are populated with the values defined in the custom type. Both fields are editable.
Note: If the Archive Type is not empty, the system will unpack the content of the Artifact while transferring the Artifact to the Target.
- Select the folder where you want to store your Artifact.
- Enter the remote artifact checksum file to be downloaded (See: GetArtifact Action in Component Workflows).
- Click Create.
Changing the Properties of an Artifact
The properties of an Artifact are defined by the custom type of the Artifact Source.
To change the properties of an Artifact you can use:
- The sidebar next to the Artifacts list.
- The Properties section of an Artifact.
The following properties are displayed:
-
Basic attributes of the Artifact. You can edit the Name, which must be unique within the Artifact Source.
- Source
Path to the remote file/directory and checksum to be downloaded. The archive type must be also selected.
-
Recent Installations
Latest deployments of the Artifact. To see all installations click Show All Installations.
-
Artifact Files
List of files of the Artifact. Click a link to access the file stored in the Artifact Source.
Note: The action executed (for example, open, download, open in another program, and so on) depends on your browser configuration.
If a checksum has been defined, it is displayed below the file path.
-
Sealed
If the Artifact properties can be modified.
-
Actions are located in the toolbar. They can be also triggered from the context menu displayed after right-clicking the entity. You can trigger the following actions (depending on your permissions):
- Duplicate: see Duplicating Artifacts.
- Delete: see Deleting Artifacts.
- Archive: archives the selected entity. If an entity is archived, Restore is available (see Archiving Entities)
-
The changes made to an artifact or to an artifact file are displayed in the artifact history (for example, upload or deletion of an artifact file, change in artifact file status, and so on).
Assigning Artifacts to Components
Important! Artifacts can be also assigned to nested Components. See: Working with Nested Components.
- Open the Release Automation perspective.
- Click the Applications tab.
- Double-click an Application to open it and select a Component.
- Click the Artifacts tab at the top of the view.
- Click the Assign button in the toolbar. The Assign Artifact dialog is displayed.
- Select an Artifact.
- Click Select.
Assigning Artifacts to Package Components
- Open a Package and click the Components tab.
- Click the Select Artifact inline button on the right side of the page.
- Select the Artifact that you want to assign to the Package Component.
Important!
- You can select both Artifacts which have been already assigned to the Component or unassigned Artifacts.
- The latest Artifact assigned to a Component on which the user has the required permissions will be auto-assigned to a Package during creation.
- Click OK.
Duplicating Artifacts
- Select the Artifact you want to duplicate and click the Duplicate button in the toolbar. The Duplicate dialog is displayed.
- Optionally, enter a new name for the Artifact. It can only contain alphanumeric characters, blanks, ., -, _, @, $, #.
- Clear the checkbox to remove the component assignments from the source artifact.
Important!
- Passwords are not copied to the new Artifact.
- Duplicating an Artifact also duplicates its artifact files. Therefore, any changes made to the artifact files in the duplicate Artifact do not affect the artifact files in the original Artifact.
Deleting Artifacts
You can delete an Artifact from the Artifacts list of an Artifact Source. Click the Delete button in the toolbar.
Notes:
- The Artifact is not deleted from the system.
- You may only delete the entity when you have the appropriate permission on the containing folder (see Security and System Hardening) and all of the listed conditions are met.
Conditions to delete entities of type Artifact
- No referenced by any Executions
- No referenced by any Packages
Deleting Artifact Files
Important! This action can only be executed with the RM Repo Artifact Source. For more information, see: Consolidating Artifacts in CDA with the RM Repository
- Open the Release Automation perspective.
- Click the Applications tab.
- Double-click a Component to open it.
- Click the Artifacts tab. The list of Artifacts that are defined for the current Component is displayed.
- Double-click an Artifact to open it.
- Select a file or folder.
- Click Delete in the toolbar.
GetArtifact Action in Component Workflows
The GetArtifact Action is included by default in all Component Workflows created with the option Create a blank Component Workflow (see: Adding Component Workflows) or with the Application wizard (see: Creating Applications Using the Wizard).
For compliance purposes, this Action downloads the Artifact and the checksum file from the external artifact source (repository) and transfers them to the local agent. The values retrieved from the repository will be then compared with the values calculated by the system. If the values do not match, you can decide if you want to resume the deployment or cancel it.
You can do the following:
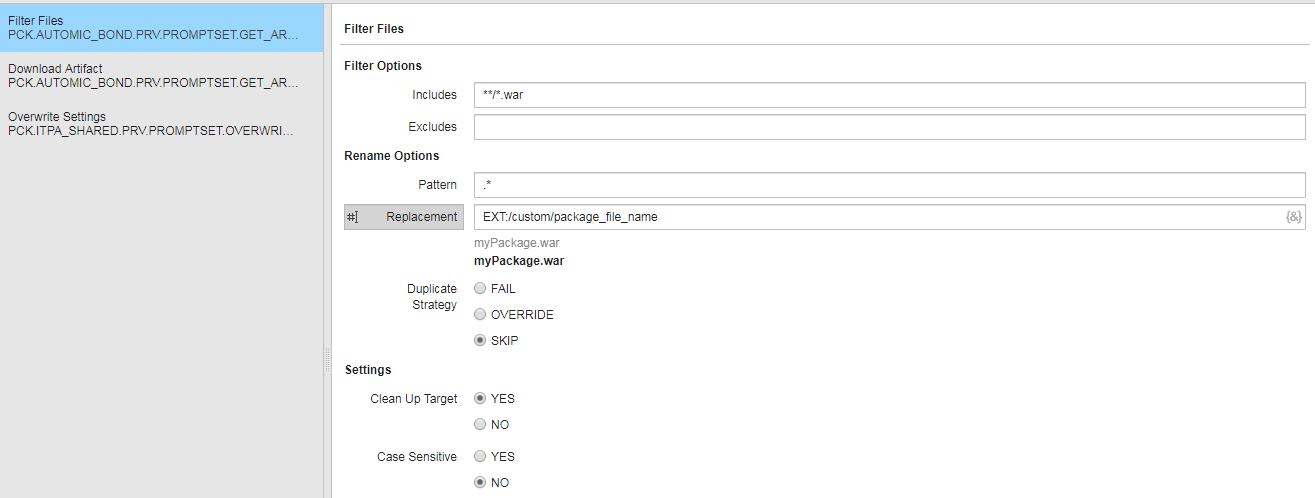
- Define if the checksum should be skipped (if there is no checksum available), ignored or required in the Download Artifact PromptSet of the Action.
- Set filter options in the Filter Files PromptSet of the Action.
- Define which files you want to be transferred or ignored in the Includes and Excludes fields. Wildcards are supported.
- Rename Artifacts. To do so, enter the new name in the Replacement field of the Rename Options section.
- Define whether you want to use the remote staging feature for transferring the Artifact in the Enable Staging Prompset of the GetArtifact Action. If you select the yes option, you must define an Agent and base directory in the Remote Staging section of the Target.
- In the Force Download PromptSet, you can define how to proceed in case an Artifact is already stored in the Artifact folder: if the Artifact should be replaced or if the step should be skipped.
- You can enter SUDO options in the PromptSet to download the Artifact to your UNIX machine in SUDO mode.
Note: Click the image to expand it.
For more information, see GetArtifact Action.
Cleaning Up Unused Artifacts
For more information about how to configure an automated process to delete unused Artifacts, see DB Cleanup Configuration
Sealing/Unsealing Artifacts
You can seal Artifacts to prevent their properties from being modified.
Important!
- Administrator rights are required to unseal Artifacts.
- Artifacts cannot be unsealed if they are being used in an active execution. For more information, see: Executing Application Deployments.
To Seal/Unseal Artifacts
- Open the Release Automation perspective.
- Click the Applications tab.
- Double-click a Component to open it.
- Click the Artifacts tab. The list of Artifacts that are defined for the current Component is displayed.
- Select an Artifact from the list and click the Seal/Unseal button in the toolbar.
See also: