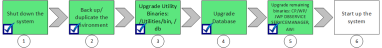
5 - Upgrade the Remaining Binaries
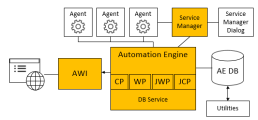
System Overview
Click the image to expand it.
To Upgrade the Remaining Binaries
-
Upgrade AE and Service Manager.
-
Upgrade the Automic Web Interface.
Upgrading ECC to AWI 12.1
Upgrading an existing ECC installation to the new release upgrades the AWI framework and all its plug‑ins at the same time. Use the same steps to install hot fix packages between releases.
Stop the Apache Tomcat Service
- Open your Windows Services manager.
- Stop the Apache Tomcat service.
These steps are optional. You can make a safety copy of your entire ECC installation, or just the configuration files. Although you can use very little of the previous configurations in the new version, you might find it helpful to have a copy for later reference when you configure the upgrade.
- To backup your whole ECC installation, go to your Tomcat installation, open the webapps folder and make a backup copy of the entire Enterprise.Control.Center folder.
- To backup only the configuration files, go to the folder where you have the current ECC version installed and make a backup copy of the folder webapps/<ECC>/config.
Upgrade the Apache Tomcat web application server where you have ECC currently installed to the latest version that complies with the new release.
- Check the System Requirements in our online database, the Automic Compatibility Matrix to see which version of Tomcat you need.
- Go to the Tomcat home page and then download and install the required version. You will find the installation instructions and other relevant information on their home page.
http://tomcat.apache.org/index.html
For Windows: Download the package called "32-bit/64-bit Windows Service Installer." This will install Tomcat and a Windows service for it.
Restart the Apache Tomcat Service
- Open your Windows Services manager.
- Stop and restart the Apache Tomcat service.
Deploy the new version of the AWI on your application server.
- (Optional) Rename the WAR file to AWI.WAR, keeping the "war" extension. The name of the WAR file will also be the context path of your AWI installation.
-
Do one of the following:
Tomcat installation
On the server where you have the Tomcat installed, copy the WAR file to the webapps folder of the Tomcat installation. If the Tomcat is running, the WAR file will be deployed automatically, creating a folder with the same name.
Do not delete the WAR file! If you do, the application server will also remove the corresponding subfolder, which also undeploys the AWI!
WebSphere installation
Please refer to the IBM WebSphere official documentation for details.
- Configure your upgraded AWI.
If you made a backup before you started the upgrade, then you can retrieve the following files and settings from the backup files from the previous webapps/<ECC>/config folder:
In the new webapps/<AWI>/config Configuration from ECC that can be used for AWI 12 uc4config.xml You can replace the new file with your backup. However, if you have more than one AE system connection defined, be aware that if the configuration.properties file has the setting the automationengine.index=0, then users will be able to log into only the first connection that is defined in the file. If you want to keep these settings in both files, then make sure to move the preferred connection to the first place in the uc4config.xml.
configuration.properties Do not replace the file in your new installation with your backup. Instead, define the file as described in this guide. However, you can refer to your backup files for the following two parameters, which may have optionally been defined in ECC:
- defaultHomeDashboard (This would be the "dashboard" attribute in the navigation.xml file.)
- customHomeDashboardsFolder (This would be from the previous configuration.properties file.)
If you had changed the default setting for the severity level of ECC event messages (DEBUG) for the root element, then you might want to make the same change for AWI 12.
The "theme" folder If you had customized the color or banner logo in ECC, then copy the contents of your backed up webapps/<ECC>/config/theme folder to the folder of the same name in AWI 12.
For more information see the topics "Customizing the AWI User Interface" and "colors.properties."
-
Configure and Start the Java Work Process (JWP).
As of v12 the installation of JWP is mandatory.
General
As of v12, several important functions in the Automation Engine and thus AWA depend on the JWP being installed and running.
Therefore the JWP's installation is mandatory.As of v12.1.1, it is mandatory to use and enable the JDBC section in the UCSRV.INI file.
Files Provided
The JWP is provided in the same directory as all the other Automation Engine files.
The directory /configuration/ is created automatically when the JWP is first started and contains the OSGI bundle's cache.
To Install the JWP
Unpack the files
In Windows, the JWP files are automatically copied from the SETUP.EXE program to the BIN directory. In UNIX, the files are located in the respective TAR archive.
Copy the provided "plugin" and "lib" directories into the BIN directory of the Automation Engine.
If the BIN directory for this installation already has a "plugin" and/or "lib" directory make sure to delete them before copying the new ones.
The subsequent installation steps depend on the database type used.
Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) (Optional - Only for SSO)
-
Install Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) Unlimited Strength Jurisdiction Policy.
The JCE Unlimited Strength Jurisdiction Policy has to be installed on the machines where:
- The Automic Web Interface runs.
- The Automation Engine (JWP) runs.
Download at Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) Unlimited Strength Jurisdiction Policy
For IBM Java, you must use the policy files of IBM. The unlimited jurisdiction policy files are located in directory SDK /demo/jce/policy-files/unrestricted/. See https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/en/SSYKE2_7.1.0/com.ibm.java.security.component.71.doc/security-component/sdkpolicyfiles.html
The Readme file contains the installation instructions on how to copy the .jar files to appropriate location (e.g.
<java-home>\lib\security). If there are multiple Java installations on the same computer, setting up a policy file for all installations is recommended.
SSL certificates for LDAP (Optional)
In order to use SSL, the certificate(s) of the LDAP server must be available to the Java Work Process.
Find the installation steps below.The JWP uses the default keystore file "cacerts" in the lib/security directory of the JRE.
Keystore file configuration options
Using an alternative keystore file:
If you want the JWP(s) to use an alternative keystore file, you have to define the file name and path to a centrally stored file in the key JWP_KEYSTORE_PATH, in the UC_SYSTEM_SETTINGS variable.
In case the defined path is not accessible or invalid, a log message will be written to the default log location and the JWP will use the default keystore file.
Creating an individual keystore file using the JWP:
If you want to use an individual keystore file, you can create it using the following command:
java -jar ucsrvjp.jar -installcert host:port keystorePathIn case the defined path in keystorePath does not exist, the JWP creates a new keystore file in that location. You can then define a password for that keystore file.
Using an alternative password for keystore file access:
The default password used by the JWP is the default password of the JRE keystore. If you want the JWP to use a different password, you have to define a Login object containing that password by following these steps:
- Create a Login object (or use an existing one).
- In the UC_SYSTEM_SETTINGS variable, using the key JWP_KEYSTORE_LOGIN, enter the name of that Login object.
- Open the referenced Login object, select the Login tab and add a new row there.
- In the column Name, select "*", in the column Type select "JWP_KEYSTORE".
- The Login info is optional for this function, but as this column cannot be empty by default, you have to enter something here.
- Enter the password you chose for the keystore file.
Adding the certificates
-
Add certificates using the keytool.
- To use the default keystore of the JRE, go to the jre\lib\security folder of the Java installation and import the certificate with the keytool command:
- To use your own keystore file defined in the variable UC_SYSTEM_SETTINGS using the key JWP_KEYSTORE_PATH, go to the defined path and import the certificate with the keytool command:
keytool -keystore cacerts -importcert -alias ldapServer -file certficate.cer
keytool -keystore <keystore> -importcert -alias ldapServer -file certficate.cer
When prompted to trust this certificate respond by typing "Y".
-
Add certificates via download.
- Another option to install the certificate is the command line parameter -installcert of the Java Work Process.
- This assumes that the Java Work Process has write access to the cacerts file of the Java installation.
- This command detects the path of cacerts, connects to the specified host and port and tries to create an SSL connection.
- This command to add a certificate via download will set an optional parameter for the file name of the keystore:
java -jar ucsrvjp.jar -installcert <host>:<sslport>
java -jar ucsrvjp.jar -installcert <host>:<sslport> <keystorePath>
When the parameter "keystorePath" is valid but the file doesn't exist, JWP creates a new keystore file in the same location.
During this process the user can define an individual password.If a certificate is missing, the message "unable to find valid certification path to requested target" is printed and the missing certificate is downloaded and stored in the cacerts file.
Start the JWP
Use this kind of command to start the JWP via the command line
java -Xmx512M -jar ucsrvjp.jar -IC:\temp\ucsrv.ini
The file "ucsrvjp.jar" is provided in the same directory as the other Automation Engine files. It is used exclusively to start the JWP.
The JWP can also be started via ServiceManager.
java -Xmx512M -jar ucsrvjp.jar -svc%port% -IC:\temp\ucsrv.ini
The -svc parameter should be omitted when starting directly via the command line.
The parameter -I to specify the INI file is optional. If the parameter is missing, the JWP attempts to find the file "ucsrv.ini" in the current working directory (= directory in which the file "ucsrvjp.jar" is located).
-
-
Configure and Start the Java Communication Process (JCP).
The files needed for JCP are the same as the files provided for JWP in the same directory as all the other Automation Engine files.
Since the JWP's installation is mandatory and the files necessary for the JCP are the same as those used to install the JWP, there is no need to unpack any files nor to carry out any other installation step.
The JCP installation is relevant for the AE REST API as well as for the advanced object search. Therefore, make sure to configure the REST section of the Automation Engine configuration file (ucsrv.ini) accordingly. Otherwise the AWA object advance search will not work.
We recommend using HTTPS.
HTTPS/SSL set up for AE REST API
In order to use HTTPS you need to set the parameter sslEnabled to 1 and continue with the setup of the following parameters in the Automation Engine configuration file (ucsrv.ini):
-
keystore
This parameter is mandatory and needs to point to the correct target, otherwise the JCP server will terminate.
-
keystorePassword
-
keyPassword
The keystorePassword and the keyPassword can be encrypted with the UCYBCRYP Utility.
Adding the certificates
JCP uses keystore as defined in the Automation Engine configuration file. For additional information as well as information on adding certificates, see https://www.eclipse.org/jetty/documentation/current/configuring-ssl.html.
Start the JCP
Use this kind of command to start the JCP via the command line:
java -Xmx512M -jar ucsrvjp.jar -IC:\temp\ucsrv.ini -rest
The file "ucsrvjp.jar" is provided in the same directory as the other Automation Engine files. It is used exclusively to start the JWP and JCP.
The JCP can also be started via ServiceManager.
java -Xmx512M -jar ucsrvjp.jar -Iucsrv.ini -svc%port% -rest
The -svc parameter should be omitted when starting directly via the command line.
The parameter -I to specify the INI file is optional. If the parameter is missing, the JCP attempts to find the file "ucsrv.ini" in the current working directory (= directory in which the file "ucsrvjp.jar" is located).
Setting Up Multiple REST API Processes
When using multiple JCPs it is imperative that each JCP uses its own Automation Engine configuration file (ucsrv.ini).
If only one INI file is used for more than one JCP, the first one will connect successfully while the others will terminate upon trying to register the same REST port if both run on the same node. An error message is written to the JCP's log file stating the reason for termination.
The AE REST API can be installed multiple times, either with different port numbers on one node or on different nodes (in this case the same port number may be used).
The following scenarios are supported:
Single JCP
In this case a single JCP is used and all REST requests are sent to this single AE REST API instance. This means that no fail-over capabilities are provided and no AE REST API is available if the JCP is down.
Clustered JCPs
In this case two JCPs are used in a cluster but only one of both is available at the time, thus providing fail-over capabilities. All REST requests are sent to only one of the two AE REST APIs, depending on their respective availability.
To use this configuration a JCP needs to be installed on each node but both JCPs share the same Automation Engine configuration file (assuming the cluster shares the same installed resources). If a virtual IP is being used, both JCPs can be reached via the same IP address. This means the endpoints have the same base URI: http(s)://{host}:{port}/ae/api/v1/{client}/...
Please note that a configuration with multiple JCPs is not intended for load balancing purposes.
-
Upgrade Progress
Next steps:
Previous steps: