The following document contains detailed instructions on how to set up single sign-on (SSO) for the Automation Engine system. Single sign-on makes it possible to log in without having to enter login details (user, department, password).
Kerberos KDC (Key Distribution Center) is used for single sign-on. The OS user under which the AWI has been launched is used for authentication.
These installation instructions apply to Windows and UNIX.
Installation steps for Automation Engine and AWI
1. Create a registry key for Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) access
The following change must be made to the Windows Registry on any Windows server that runs the AWI server (Tomcat).
The registry key is required so that the Kerberos Java implementation can use an existing TGT. The TGT will be generated by logging in to the operating system.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\Kerberos\Parameters]
"allowtgtsessionkey"=dword:00000001
2. Install the Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) Unlimited Strength Jurisdiction Policy
The JCE Unlimited Strength Jurisdiction Policy has to be installed on the machines where:
- The AWI runs
- The Automation Engine (JWP) runs.
Add JCE to Tomcat jre/lib/security folder: Download from Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) Unlimited Strength Jurisdiction Policy.
The Readme file contains the installation instructions. If there are multiple Java installations on the same computer, setting up a policy file for all installations is recommended.
3. Kerberos configuration file on the AWI server
The krb5.conf file should be created in all other cases. The location of the configuration file is <java-home>/lib/security/krb5.conf (same location as the JCE)
The exact search sequence is described under https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/security/jgss/tutorials/KerberosReq.html in the section "Locating the krb5.conf Configuration File". The Kerberos documentation describes how to set up this file.
Example:
[libdefaults]
default_realm = DOMAIN.SAMPLE
default_tkt_enctypes = rc4-hmac
default_tgs_enctypes = rc4-hmac
permitted_enctypes = rc4-hmac
[domain_realm]
.domain.sample = DOMAIN.SAMPLE
[realms]
DOMAIN.SAMPLE = {
kdc = servername.domain.sample
admin_server = servername.domain.sample
}
Restart Tomcat.
4. Enable KDC in the AE system-wide settings
In the UC_SYSTEM_SETTINGS file, set KDC to Y to enable Kerberos Distribution Center (KDC) authentication for a whole system.
Installation steps for the JWP
Generate keytab file
The following steps must be performed by the domain administrator (for each AWI host):
1. Create a service user in the Microsoft Active Directory
Each host running the AE server processes must have its own associated service user in the Microsoft Active Directory. This user will be used for authentication between the JWP and the Microsoft Active Directory.
Create a new service user in the Microsoft Active Directory for each host where the Automation Engine runs. The user password should not expire. Activate the account option "This account supports Kerberos". See also Windows Configurations for Kerberos Supported Encryption Type
2. Create Service Principal Name (SPN) on the Kerberos Administration Server
To implement single sign-on for web applications (such as AWI or ARA), you need a keytab file with HTTP as Service Principal Name.
For example:
HTTP/winhost01.domain.sample
In this example, winhost01 is the host on which the AWI (Tomcat) is installed.
Automic recommends creating SPNs for each AWI host (one SPN with the host name and one with the fully qualified domain name).
Make sure you pay attention to upper and lower case letters when creating SPNs. Otherwise, the name may not be found in the Kerberos database.
The realm is optional. If it is not specified, the default value from the configuration file krb5.conf will be used. In Windows, the Kerberos realm name is the domain name (DNS suffix) in upper case letters (such as DOMAIN.SAMPLE)
Also see: Detailed description of Kerberos principals.
Example:
AEServer01/winhost01.domain.sample@DOMAIN.SAMPLE
The SPNs must be assigned to the previously created KDC service user.
If the Automation Engine runs on more than one host, then the above steps must be performed for each of the AE hosts. Each AE host must have its own associated service user, and the SPNs must be created for each of these service users. In Microsoft's Active Directory, the command "setspn" can be used to create SPNs. As stated above, creating an entry for the host name and one for the fully qualified domain name is recommended.
Example:
setspn -s AEServer01/winhost01.sample.host@DOMAIN.SAMPLE ServiceAccount01
setspn -s AEServer01/winhost01@DOMAIN.SAMPLE ServiceAccount01
setspn -s AEServer02/winhost02.sample.host@DOMAIN.SAMPLE ServiceAccount02
setspn -s AEServer02/winhost02@DOMAIN.SAMPLE ServiceAccount02
3. Generate keytab file on the AWI server
In Microsoft Active Directory, you can use the command "ktpass" to generate a keytab file. The SPN, KDC user, KDC user's password, path/file name of the keytab file and the parameter /mapuser must be specified.
ktpass /princ HTTP/awihost.domain.sample@DOMAIN.SAMPLE /mapuser ServiceAccount01@DOMAIN.SAMPLE /pass ServiceAccountPass /mapop set /crypto all /out c:\temp\ae.keytab -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL
The keytab file C:\temp\ae.keytab will then be created.
You can also create the keytab file on the Kerberos Administration Server.
Details of "ktpass" command syntax: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc753771.aspx
AWI Deployed on Different Hosts
If the AWI is deployed on different hosts, then the steps for generating the keytab file (steps 2 and 3) must be performed for each host name.
This will result in additional keytab files. However, the JWP requires exactly one file, which means the entries must be merged into one file.
On UNIX you can use the application 'ktutil' with the following commands:
ktutil
rkt keytab1.keytab
rkt keytab2.keytab
wkt merged.keytab
Thereby a new file named "merged.keytab" is being created which contains the entries of keytab1 and keytab2.
Since the Java for Windows has no merge parameter, the simplest solution is to merge the two files using 'ktutil' on a UNIX system and then transfer the merged file to your Windows installation.
4. Specify the keytab file
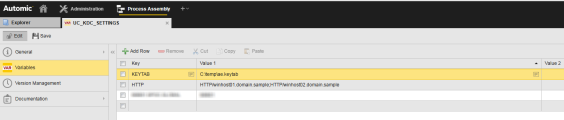
Now enter the path and file name of the generated keytab file in the Variable object UC_KDC_SETTINGS which is located in client 0.
Specify the value "KEYTAB" in the Key column of the Variable object and the key tab file in the column "Value 1".
Make sure that you restart the JWP after changing a setting in a system variable.
If there are multiple JWPs on different hosts, the keytab file must be located in the same directory on all hosts. If the file is missing on one or more hosts, login will not always work.
The SPN name must also be entered in the variable UC_KDC_SETTINGS using the "HTTP" key. If several AWI/ARA installations are available for an Automation Engine system, then other names separated by a semi colon can be added.
Example:
HTTP/winhost01.domain.sample;HTTP/winhost02.domain.sample
Enabling single sign-on in AWI
When users log into AWI, usually the login is authenticated by the Automation Engine that the instance is connected to. If single sign-on (SSO) is set up in the Automation Engine for the connection, you can enable SSO for users in AWI.
What you have to do
-
In your AWI instance, set the sso.enabled property to "true" in the configuration.properties.
- In each user definition, select LDAP Connection on the General > User Information page so that the user's email and name are synced.
Results
When you, or any user, logs in the first time, the login window will have an additional Use Kerberos login option.
- If you do not select this option, you will need to log in with your AE user information (Name, Department, and Password).
- If you select the Use Kerberos login option, then the Name, Department, and Password fields disappear, and an additional Enable autologin option appears.
- If you do not select the Enable autologin option, then when you log into AWI, you can change your session options (Language, Connection, Client, Session Color), but you do not have to enter your user information or password.
- If you want to skip entering any login information in the future, then first select your session options and then select Enable autologin. The next time you start AWI, you will bypass having to enter login information.
Tip: If you want to change the session information in the future, empty your browser's cache. When you start AWI the next time, you will have the full login window again.
SSO (Kerberos) Enabled
Kerberos Selected 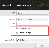
Losing Kerberos Connection
If you lose Kerberos connection, the login page will appear, regardless of your previous choices, and you will see the following warning message on the login page:
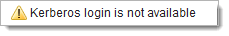
This can happen if you log in from a computer or server that is not in the Windows domain where Kerberos is installed or if there is a problem in the configuration or Kerberos. In the meantime, you can log in with your Automic user name and password.
Reason: When an AWI instance is set up for SSO, authentication is passed onto Kerberos. If Kerberos is not in the Windows domain, then Windows tries to authenticate with Windows NT LAN manager (NTLM) which cannot process the Kerberos authentication information. The login defaults to the standard Automic login, which is described in Using the Default AWI Login.
Users for Authentication
Following successful completion of the configuration, the corresponding users must be created in the clients of the Automation Engine system.
The user names must correspond to those of the OS users who should be granted access via single sign-on.
The department is irrelevant as long as the user name is unique for each client. If there are two or more users with the same name but a different department, each of these departments must be assigned to a domain in the variable UC_KDC_SETTINGS.
Single sign-on login will fail if no User object exists in the selected client with the same name as the OS user, such as the one used for launching the AWI.
Example:
The AWI is launched in Windows under the user "test/local".
AE system TEST, client: 100
If no user object with the name "TEST/*" (department irrelevant) exists in client 100, single sign-on login is not possible.
If there are several users in client 100 with the name "TEST/*" (for example, "TEST/DEV" and "TEST/LOCAL"), the departments (as described above) must be assigned to the domains of the OS users. If departments are not assigned, login will also fail.