SNMP can be used to monitor the various conditions which occur within an AE system. Its activities include monitoring the availability of the Automation Engine and agents, active notifications or blocking tasks.
The following illustration explains the interaction of AE and SNMP:
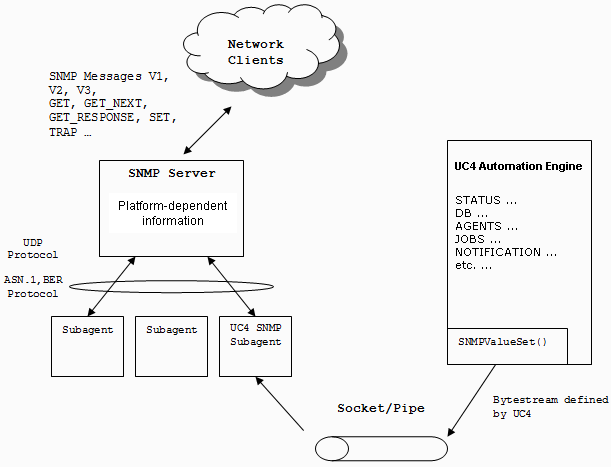
With the SNMP connection being activated, the relevant AE system monitoring values are sent to the AE SNMP Subagent. It stores this information in its MIB and makes it available for the SNMP Masteragent. The MIB content is write protected, the AE SNMP Subagent prevents values from being modified with the SNMP command SET.
For applications (e.g. HP OpenView Operations), there are two methods to obtain information:
- The applications can periodically request information via the SNMP Masteragent which communicates with the AE SNMP Subagent in order to obtain the relevant values.
- Events of special importance which occur in the AE system trigger SNMP traps. The AE SNMP Subagent immediately forwards them to the SNMP Masteragent to ensure that the applications can directly obtain the required information.
In particular situations, the Automation Engine generates predefined traps., see Generated SNMP Traps. You can also send traps using the script statement :SEND_SNMP_TRAP.
Note: Specify in the AE SNMP Subagent's INI file whether the MIB should be loaded and/or traps be sent. By default, both is done. It is recommended to deactivate MIB loading if you intend to use traps only in order to avoid unnecessary performance loads. The corresponding parameter processing= is available in the section [SNMP].
Masteragent Mode On
The AE SNMP Subagent under UNIX is able to act as SNMP Masteragent with the advantage being that no SNMP service must be configured. For more information, see Agent Mode on UNIX.
See also: