
|
Context Menu of the Explorer |

Explorer |
Transport Case |

|
 Recycle Bin
Recycle BinThis document describes how to use the Recycle Bin in the Explorer. The Recycle Bin includes objects that have already been deleted.
The following methods can be used to delete objects:
 button in the tool bar.
button in the tool bar.Note that objects that have been specified for transport and are located in the Transport Case cannot be deleted.
Whether a query is made when an object should be deleted depends on the specifications that have been made in the UserInterface. A query always displays if an object is used in other objects.
Deleted objects are stored in the Recycle Bin and obtain an extended name. A system-internal number is appended to the object name. You can restore deleted objects by highlighting one or more objects in the Recycle Bin and selecting Restore in the Edit menu of the UserInterface or context menu. The deleted object is restored in "No Folder". You can also restore an object directly to a specific folder. Drag and drop the object from the open Recycle Bin to the Explorer folder. A requirement for restoring objects is that no other object of the same name can be created after the deletion process.
The objects in the Recycle Bin can be displayed with large symbols, as a list, or with details. Additionally, you can sort the objects by their name, object type, object title and date of deletion. Do so using the command buttons in the tool bar, the View menu of the UserInterface or the context menu (right-click without highlighting an object). Simply click the column title in order to sort them in ascending or descending order.
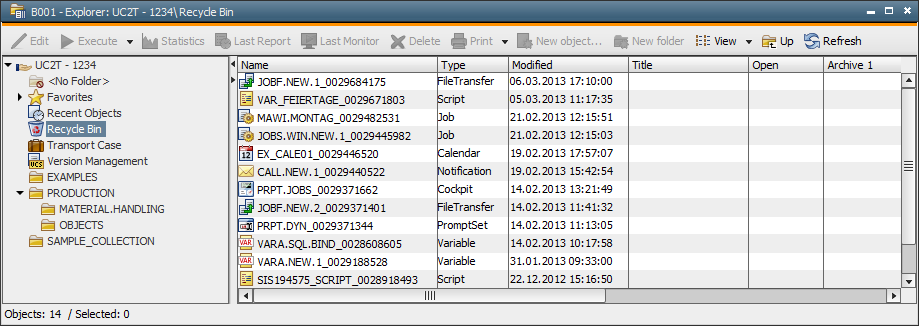
The administrator can limit the number of objects that should be displayed in the Recycle Bin by using the entry TRASHBIN_SHOW_MAX in the variable UC_SYSTEM_SETTINGS.
Deleted objects that have been archived using the utility AE DB Archive are not available in the Recylce Bin.
Only privileged users have access to the Recycle
Bin.
Users who do not have "Access to the Recycle Bin" cannot (or
only partially) use the described functions, menu commands etc.