
|
Evaluating with Linear Regression |

Methods of Runtime Evaluation |
Adaptive Evaluation |

|
This method takes the maximum value from the possible 25 existing real runtimes (RRT) of a task.
If a large number of runs is to be calculated, the estimated runtime immediately adjusts to increasing runtimes. However, if the real runtime decreases, this results in a slow adjustment.
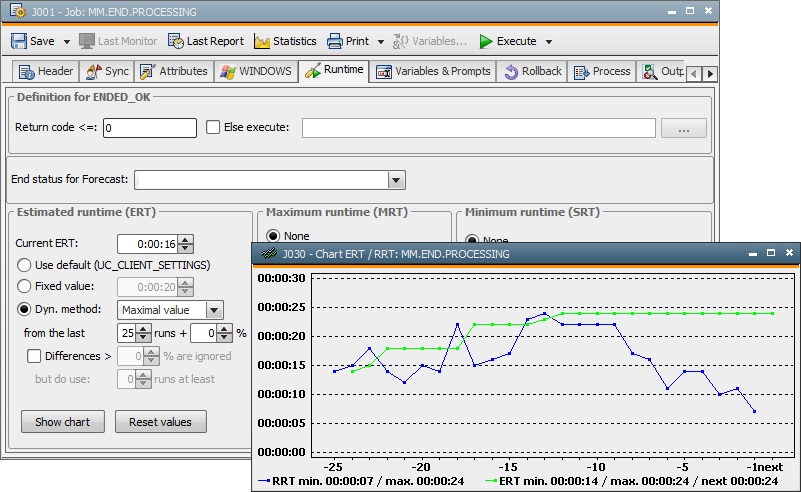
In order for the decreasing tendencies to be recognized more quickly, the number of runs to be calculated can be reduced.
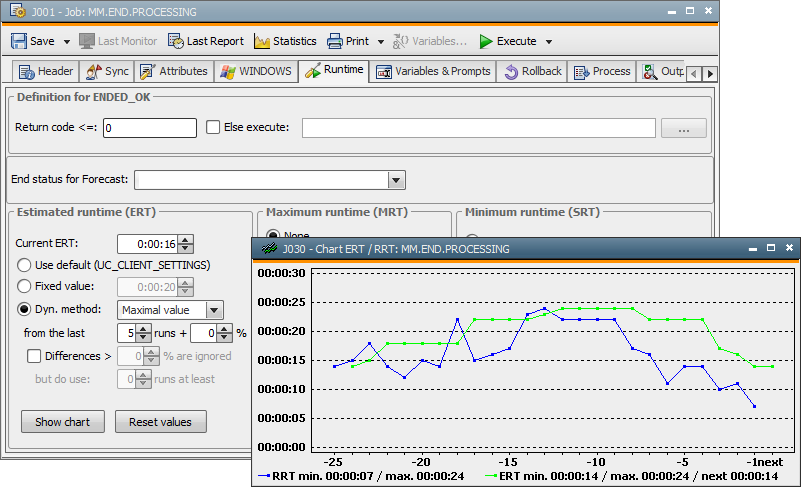
To preserve a distance between estimated runtime and real runtime, it is possible to specify a correction value in percent. This value is added to the estimated runtimes. This allows the setting of an alarm only with extreme increases in runtime.
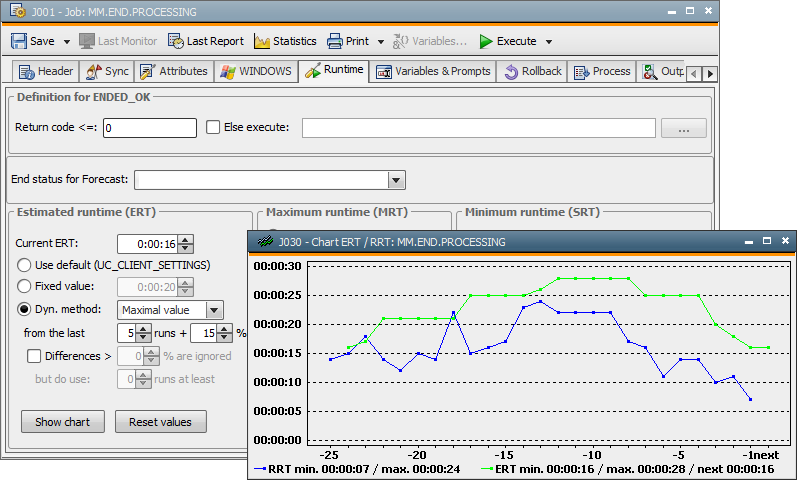
In order to avoid the evaluation of extreme deviations, a maximum deviation in percent can be set for calculations. If the real runtime exceeds this limit, it will not be taken into account in the calculation of the ERT. The minimum number of runs can also be specified here.