
|
Roll |

Calendar |
Client |

|
 Documentation Tabs
Documentation TabsDocumentation tabs are user-defined and client-specific tabs that can be assigned to all objects.
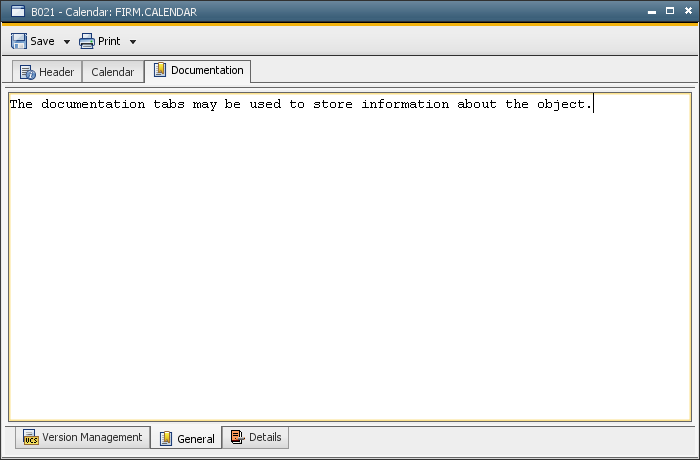
All Documentation tabs that have been defined by the administrator in the variable UC_OBJECT_DOCU are shown. Note that imported objects have their own documentation tabs.
The Version Management tab displays the stored object versions if this function has been activated.
Each of these tabs can also be displayed in structured form. Structured Documentation can be used to split complex object information in well-arranged parts. Each documentation element can be used to store texts, but also to define attributes.
Defining links (such as to files, folders or to documents in the Intranet and Internet) is also possible in structured documentation. Files are then displayed with the associated program, folders are opened, URLs call the standard browser etc. The particular actions depend on the installed programs and the user's PC configurationA set of constituent components that make up a system. This includes information on how the components are connected including the settings applied..
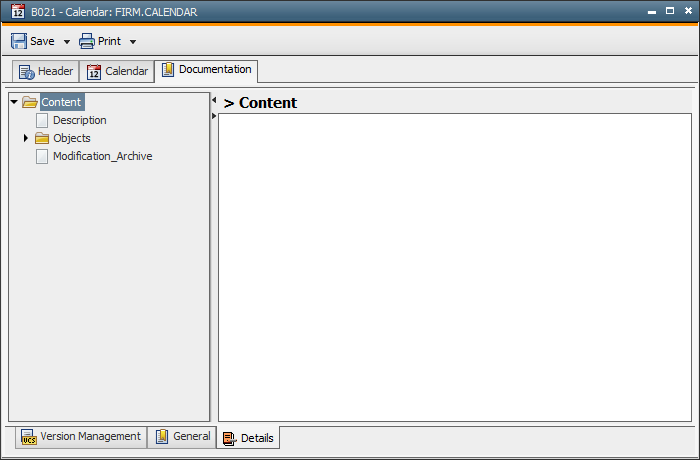
New Documentation tabs initially only include the "Content" folder. This is your starting point for creating a further structure. To create and edit this structure, you can use the following popup-menu commands :
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Add attribute |
Creates a new attribute in the highlighted element. |
|
Add node after |
Inserts a new element after the highlighted element. |
|
Add node before |
Inserts a new element before the highlighted element. |
|
Add node child |
Creates a new element one level below the highlighted element. |
|
Duplicate node |
Duplicates the highlighted element and its attributes and contents. |
|
Delete node |
Deletes the highlighted element irrevocably . |
You can create one or more attributes for each individual element. Basically, there are two different types: text and enumeration. You can add one or more of these attributes to an element. Determine the attribute's name and then select whether it is a text or an enumeration. In enumerations, you can specify the entries that should be included.
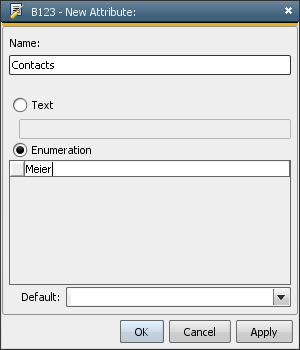
Names of elements and attributes should comply with the XML naming convention. Letters, numbers and the characters "-", ".", "_" can be used. Keep the following rules in mind:
Structured documentation can be read with specific script elements (XML_*).