An example will demonstrate how to use the AE utility UCXE???F to query the Unix file system.
The following files should be listed:
- those which are located in the home directory of the signature AE and in all subdirectories,
- those which have last been modified between 10.1.1999 00:00 and 10.7.1999 23:50 and
- those which have a file size between 1 and 9999 bytes.
The creation, the forming up and the processing of a data sequence is a complex process in which script functions and statements as well as special objects cooperate closely. The following example shows the necessary definitions for the involved objects and the corresponding script statements and their references. The example is intentionally kept small and clear to show the principles.
The AE utility UCXE???F offers wider query possibilities compared to the traditional operating system command ls. It has to be installed on the host. The question marks in the program name are placeholders for system ID and version of the Unix derivative.
|
|
Job: SC.PROCESS.UNIXFS |
|---|
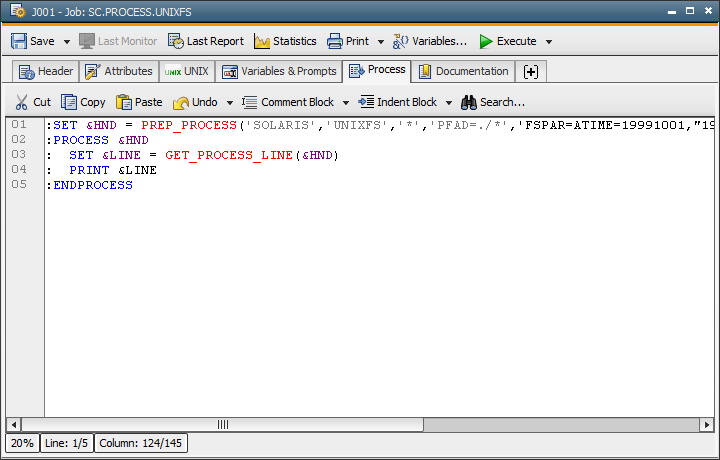
The script of the job calls the function PREP_PROCESS, which prepares the processing of the data sequence. The following parameters are passed:
- Name of the computer on which an event job is to be executed - in this case: SOLARIS.
- Type of the event job to be executed - in this case UNIXFS.
By specifying UNIXFS, the job EVENT.UNIXFS will be executed.
By default the event jobs EVENT.BS2000.CMD, EVENT.BS2000UCON, EVENT.UNIXCMD, EVENT.UNIXFS and EVENT.WINCMD are supplied with client 0000. They can be used as they are or as a template for your own event jobs. - The third function parameter specifies which lines produced by the command should be taken into account. By using the wildcard character "*", all lines will be accepted.
- With the keywords PATH and FSPAR, you specify additional parameters containing the actual queries of the Unix file system. Following the keyword FSPAR are other keywords as well as value assignments for the modification time frame, the file size and the inclusion of subdirectories. The definition of the modification time frame clearly shows the following particularities: The beginning is specified without a time. This automatically sets the time to 00:00. The end is made up of date and time specification, separated by a blank. Because blanks separate each specification within the parameter, the date and time specification has to be between quotation marks.
- The Login object AEADMIN is used.
The job SC.PROCESS.UNIXFS will then be started.
|
|
Job: EVENT.UNIXFS |
|---|

This is the job EVENT.UNIXFS from client 0000. It is supplied by default.
It is important that the check box "Attribute dialog" is checked in its Notification tab That way the Include object ATTRDIA.BS2000 is read which normally causes the start of the Attribute Dialog.
|
|
Include: ATTRDIA.UNIX |
|---|
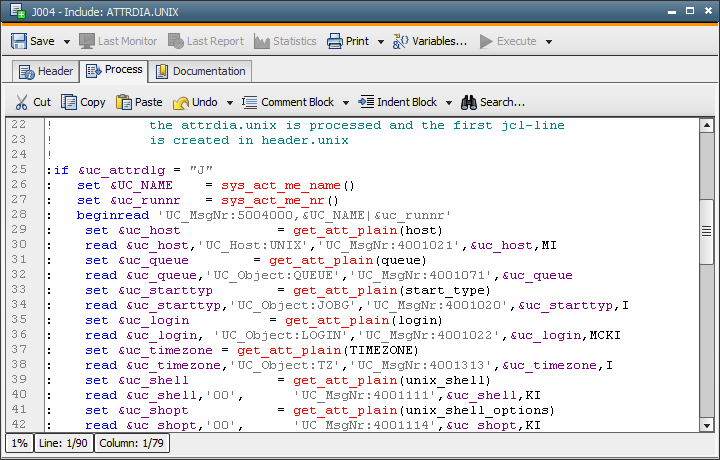
All attributes listed in the script of the Include can be supplied. The script variable &UC_USERID receives the value AE. The Attribute Dialog is not displayed because the passing of the variable contents is done internally.
|
|
Job: EVENT.UNIXFS |
|---|
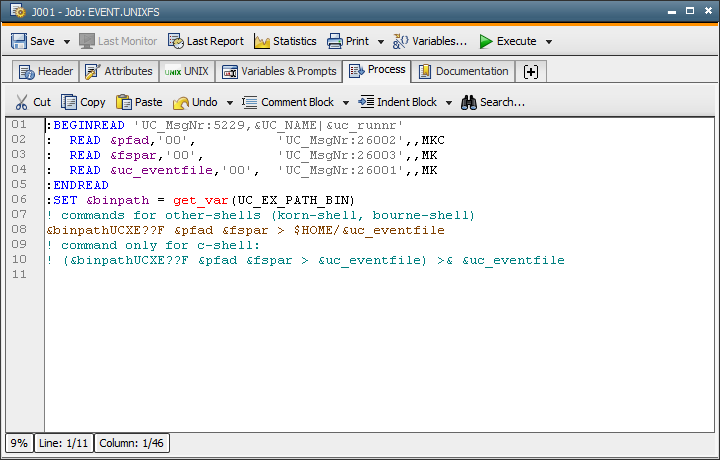
At the start of the job EVENT.UNIXFS, the script variables &PATH and &FSPAR are supplied with values. These values are defined in the parameters of the script function PREP_PROCESS of the job SC.PROCESS.UNIXFS. The AE utility is called with these specifications. It retrieves the requested information on the Unix file system. It is not necessary to replace the question marks in the program name. The utility can be called in this way after a correct installation.
The outfile is transferred to the Automation Engine via file transfer and is then available as a data sequence. The execution of the job EVENT.UNIXFS is then completed.
|
|
Job: SC.PROCESS.UNIXFS |
|---|

The function PREP_PROCESS returns a value that is a handle for information on the data sequence that will be processed.
This value is passed to the statement :PROCESS as a start parameter, :PROCESS and :ENDPROCESS then form a processing loop which, in this case, will be cycled until the end of the data sequence is reached. During each iteration a new line of the data sequence is fetched from memory. The function GET_PROCESS_LINE can - by using the current value - retrieve the content of the current line.
In the example, the current console line is written to the activation protocol.
The :STOP statement interrupts the execution and displays this activation report.