Executing Objects: The Processing Stage
Executable objects go through four execution stages. After the activation and generation stages, the task enters the processing stage. The object is prepared now, its scripts can be transferred to the Agent. The processing stage is when the task is actually executed on the target system.
Processing Stage In Detail - List
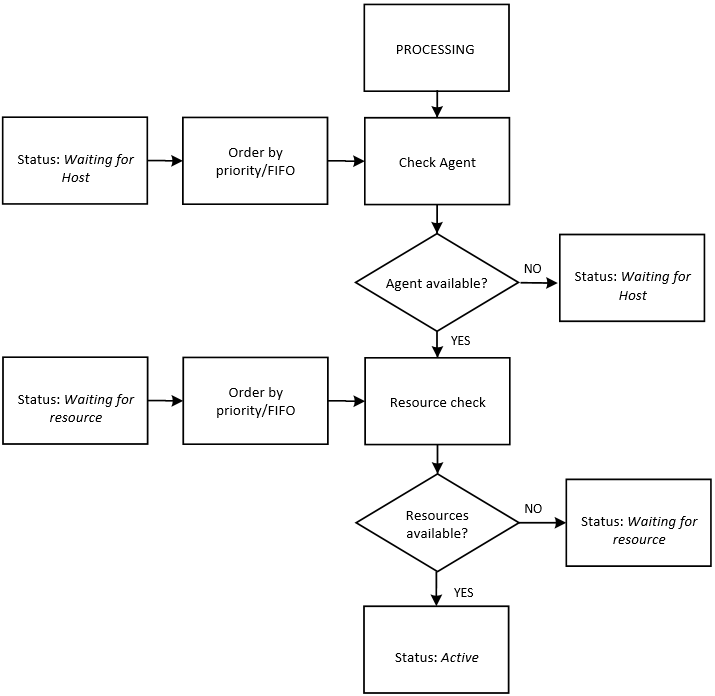
This stage starts with some validation checks and includes the following steps:
-
Agent check.
Is the Agent available for processing the task on the target computer?
- No: The task status is set to Waiting for host.
- Yes: Go to next step.
-
(For Jobs and File Transfers) Resource check.
If you have allocated a specific number of resources to the execution of the object, the system checks if there are resources available for the Agent.
- No: The status of the task is set to Waiting for resource.
- Yes: The status of the task is set to Active and processing continues with the next step.
For more information about the resources concept in the Automation Engine, see Resources when Executing Objects: Agent Workload Balancing. For more information about how and where to set this attribute, see Defining the Attributes Page.
-
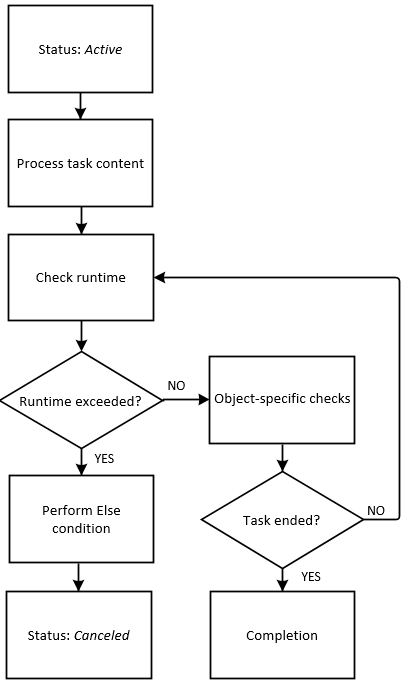
Task contents are processed.
Various actions take place now, depending on the object configuration. These are some of the most important ones:
- Notification objects are sent
- File Transfer starts
- The JCL is processed on the target computer
-
Maximum runtime check.
While the task contents are processed, the system constantly checks whether the designated runtime is exceeded.
- No: Go to next step (Completion).
- Yes: The specified Else condition is processed.
Important! Some tasks, for example Schedules (JSCH), remain active until they are ended either manually or using a script.
Processing Stage In Detail - Graphics
The following diagrams describe the steps that a task goes through during the processing stage:
Next Stage
When the processing stage has finished, the task enters the completion stage, see Executing Objects: The Completion Stage.
See also: