
|
UC_STATISTIC_OPTIONS - Controlling the Statistics Functions |

Settings in Variables |
UC_USER_LOGON - Single Logon |

|
 UC_SYSTEM_SETTINGS - System-Wide Settings
UC_SYSTEM_SETTINGS - System-Wide SettingsThis variable contains settings that apply throughout an entire AE system.
|
Validity |
Value |
Restart required |
|---|---|---|
| AGENT_COUNT_PER_IP |
This setting defines whether the IP address of agents should be used for checking the license. Allowed values: "Y" (default) and "N" |
No |
|
The maximum number of log-file changes for agents (per minute). Allowed values: 20 to n |
No |
|
|
The interval in minutes at which tasks that are waiting for the host of an agent group are checked. Allowed values: 1 to 60 |
No |
|
| BACKENDVAR_MAX_ROWS |
The maximum number of lines that a BACKEND-type Variable object returns. Allowed values: 0 to 20000 |
No |
|
The time period in days after which the log files are changed. Allowed values: 1 to 32767 |
No |
|
|
The size in MB after which the log files are changed. Allowed values: 1 to 32767 |
No |
|
| CONDITION_CHECK_INTERVAL |
The time interval in seconds at which the Preconditions tab of workflows is rechecked. Default value: 60 |
No |
| DEFAULT_REPORT_SCAN_MEMORY |
The size in MB which is requested by default for the output analysis when you read a report. Allowed values: 1 to 50
|
No |
|
The number of objects to be deleted for which the search-for-use function should be executed without a check-back being made. Allowed values: 0 to 100 |
No |
|
|
No user-defined Include objects are called in the Headers and Trailers of Job objects that run on the platforms that are defined here. Allowed values: BS2000, CIT, GCOS8, JMX, MPE, MVS, NSK, OS400, PS, SAP, SAPBW, SIEBEL, UNIX, VMS, WINDOWS or *ALL. Separate values by using commas. By default, all available Includes are executed. |
No |
|
| ERT_ADAPTIVE_JWP_TIMEOUT |
The time in minutes after a system start that the system spends waiting for the availability of a JWP in order to calculate the adaptive ERT. Allowed values: 1 to 60 |
No |
|
The object to start if a message is put into quarantine. |
No |
|
|
Interval in minutes at which external workflow dependencies are checked. Allowed values: 1 to 1440 |
No |
|
| EXT_DEP_ENDED_LOST_RUNNING |
Handling of tasks in external dependencies. N(o): Tasks with status ENDED_LOST are ignored in external dependencies. Allowed values: "N" or "Y". Default value: "N" |
No |
|
The maximum number of activities to be displayed. Allowed values: 0 to 20000 |
No |
|
|
The maximum number of Auto Forecast results to be displayed. Allowed values: 0 to 20000 |
No |
|
|
The maximum number of search results to be displayed. Allowed values: 0 to 20000 |
No |
|
|
The maximum number of statistical records to be displayed. Allowed values: 0 to 20000 |
No |
|
| GET_PROCESS_LINE_RTRIM |
The handling of blanks in a line that is read by using the script function GET_PROCESS_LINE. Allowed values: 0 and 1 (default) 0 - GET_PROCESS_LINE leaves blanks at the end unchanged. |
No |
| KDC |
Enables or disables Kerberos Distribution Center (KDC) authentication for a whole system. Allowed values: "Y[es]" or "N[o]" If this switch is not set, an internal default value of "N[o]" is assumed. |
No |
|
The time delay in minutes after which the objects' usage counter is refreshed. Allowed values: 0 to 10 |
No |
|
|
LDAP connection. Allowed values: Y and N (default value) |
No |
|
| LOG_TO_DATABASE |
This saves the server log in the AE databaseA database is an organized collection of data including relevant data structures.. Allowed values: Y (default value) and N Y - The Automation Engine's log messages are saved in the AE database. |
Server |
|
The maximum number of objects to be exported at the same time. Allowed values: 0 to 1000000 |
No |
|
|
The maximum size (KB) of the XML file to be imported. To use this setting correctly, you need also to set the maxMsgSize setting in the [TCP/IP] section of the UCSRV.INI file for the Automation Engine. Allowed values: 0 to 30720 |
UserInterface |
|
| MAX_REPORT_SCAN_MEMORY |
The maximum size in MB which is requested for reading an Output Analysis report. Allowed values: 1 to 100 |
No |
| MAXIMUM_STORE_RESOURCE_SIZE |
The maximum size of resources attached to the Storage object, in bytes. Allowed values: 0 to 71 MB (74448896 bytes) |
UserInterface |
|
The minimum interval (minutes) at which events are executed. Allowed values: 0 to 9999 |
No |
|
| MQA_COUNT_BACK |
The number of server messages to be buffered in the server computer's random access memory. Allowed values: 0 to 1000 |
No |
| MQ_BLOCK_COUNT |
The number of blocks after which the message queue is to be reorganized (Oracle databases only). Allowed values: 0 to 100000 |
No |
| MQ_CHECK_TIME |
The interval (seconds) at which message queues are checked (Oracle databases only). Allowed values: 0 to 1000000 Value 0 means that no check is made. |
No |
| OBJECT_ACCESS_CLIENT_ZERO |
Determines user access to objects in the system client from other clients in the Automation Engine system. Allowed values: "Y[es]" or "N[o]" Default value: "Y" |
No |
|
The name including the path of the generated server program library for an external passwordA secret combination of characters for a Automation Engine user. check. |
Server |
|
|
This serves to assign parameters for a password check. |
Server |
|
|
Modifies the password. Allowed values: Y (default) and N |
UserInterface |
|
|
The interval (seconds) at which the server processes attempt to establish a connection. Allowed values: 10 to 3600 |
Server |
|
|
The maximum size of the logging block (bytes) to be transferred at the same time. Allowed values: 3600 to 8000 |
Server |
|
|
The interval (seconds) at which the server processes send the log to the AE system. Allowed values: 5 to 3600 |
Server |
|
|
The number of licenses reserved for CallAPI users. Allowed values: 0 to 32767 |
No |
|
| RESOLVE_GET_VAR |
Determines the behavior of the script function GET_VAR, which was changed in version 9SP4 of the Automation Engine. Allowed values: "Y"(es) and "N"(o) "Y"(es) (default): The script function GET_VAR will show the variable's value, i.e. the variable will be resolved (as of version 9SP4). "N"(o): GET_VAR will not resolve the variable, but show the variable's name, for example: &var# (as customary in versions prior to version 9SP4) |
No |
|
The time period in seconds after which an endless loop is assumed in a script. Allowed values: 1 to 32767 |
No |
|
|
Various server settings for performance improvement and trace outputs. Format: 15-digit string By default, all options are deactivated. |
No |
|
| SHOW_REPORT_HIERARCHICAL |
By using this parameter, you can display reports as subordinate tasks in the Activity Window. Allowed values: "Y" (default) and "N" Use the Hierarchical view of the Activity Window in order to have reports displayed as subordinate tasks. This setting does not affect the statistical information as it always displays reports as child tasks. |
No |
| SMGR_PORT_RANGE |
Indication of a port number or a port area to be searched for ServiceManager services. Default value: 8871 (default port of the ServiceManager) |
No |
| SNMP_REFRESH |
This setting controls the time interval (in seconds) at which SNMP refreshes the information about blocked workflows. Allowed values: 0 (= always) to 600 |
No |
| SQLVAR_INTERNAL |
This permits the creation and editing of Variable objects of the types "SQL - internal" and "SQL - internal SECURE". Allowed values: YES and NO (default value) |
No |
| SQLVAR_MAX_ROWS |
The maximum number of lines that can be returned by SQL-type and SQLI-type variables. Allowed values: 0 to 20000 |
No |
| SYNC_BLOCK_COUNT |
The number of Sync objects whose log is to be changed per block. Allowed values: 1 - 1000 |
No |
| SYNC_CHECK_RESTART |
Determines whether Sync objects are checked when restarting a canceled job without an Abend action. Allowed values: Y and N |
No |
|
The maximum number of objects to be displayed in the Recycle Bin. Allowed values: 0 - 20000 |
No |
|
|
The output of unread administrator and security messages. Allowed values: Y and N |
No |
|
|
The maximum number of unread messages to be kept. Allowed values: 10 to 5000 |
No |
|
| VAR_SECURITY_LEVEL |
Security level for the replacement of variables in dynamic Variable objects. Allowed values: "0" (default), "1", "2" or "3" |
No |
| VARIABLE_SERVICE_CHECK_INTERVAL |
The interval in minutes at which the resolving of SQL variables is repeated if their values are not available due to an error (for example, the database is not available or incorrect data is specified in the Connection or Login object). The tasks that use these variables are in a waiting condition. Minimum: 1 |
No |
|
The maximum number of objects to be displayed in Version Management. Allowed values: 0 - 20000 |
No |
|
|
The resources that a file transfer or job is to use by default. Allowed values: 1 to 100000 |
No |
|
|
The minimum number of server processes per node name to be used as work processes (WP). Format: node name1=number;node name2=number etc. Allowed values for the numbers: 2 up to the maximum number of work processes. |
No |
|
|
The encoding of the XML files. Allowed values: ISO-8859-15 (default value), ISO-8859-1 and WINDOWS-1252 |
No |
|
|
This checks the encoding during the import process. Allowed values: "Y" or "N" Y - The import files must have the encoding which was assigned with the key XML_ENCODING. |
No |
|
| ZERO_DOWNTIME_UPGRADE |
Enables or disables a mode, which prepares the system for a version upgrade without system downtime. Allowed values: "Y" or "N" Y - A database upgrade is allowed while the system is fully up and running. New CPs/WPs can be started for working in a compatibility mode, with their peers of a pre-installed version. During the period of time where, ZERO_DOWNTIME_UPGRADE = Y the system performance will be reduced, because certain system optimizations are not possible in this mode. |
This variable is supplied in client 0000. Its settings apply for the whole AE system and can only be changed in client 0000.
AE monitors all the values that this variable includes. The administrator receives a message if an attempt is made to store an invalid value in this variable. This message is also written to the Automation Engine's log file. The default value is used instead of the invalid value. If the invalid value is a value range, the system uses the maximum value if the specified maximum value is exceeded. The minimum value is used if a value that lies below the minimum value has been found. The variable's contents remain unchanged.
An agent's license will be checked when it logs on to the Automation Engine system. By default, the system also verifies whether an agent that is already logged in uses the same IP address. If so, the agent that has newly logged on does not require a separate license.
Checking numerous agents (approx. 1,000) can increase the time that it takes to log on to the system. For this reason, you can also deactivate the IP address check by using the setting AGENT_COUNT_PER_IP.
Every agent that logs on requires its own license when you deactivate this check. Whether or not the IP address has already been used is irrelevant in this case.
AGENT_LOG_CHANGE_PER_MINUTE
The more agents an AE system contains, the higher the chance is that log-file changes are required for a large number of agents at the same time. Use the setting AGENT_LOG_CHANGE_PER_MINUTE to improve system performance by limiting the number of log files to be changed per minute.
AGENTGROUP_CHECK_INTERVAL
Tasks such as jobs or file transfers can run within an agent group. The task's status changes to "Waiting for Host" if no agent is available that is part of this agent group. The setting AGENTGROUP_CHECK_INTERVAL defines the interval at which the system checks whether a particular agent is active, and if so, it initiates the start for the waiting tasks.
The value for this setting should not lie below the interval at which the agent attempts to establish a connection to the AE system. This value can be specified with the option RECONNECT_TIME in the variable UC_HOSTCHAR_DEFAULT.
This setting determines the maximum number of lines that BACKEND-type VARA objects can return.
Note that selecting a high value can result in a longer time taken to resolve backend-type variables.
CHANGE_LOGGING_DAYS and CHANGE_LOGGING_MB
These files can be changed on a time- and size-dependent basis in order to ensure that the log files can be handled smoothly during high workload times for Automation Engines and agents. You can also archive and reorganize this data in the AE database, although the Automation Engine and the agents are active for several months without interruption in the best case.
You can also specify temporary log-file changes in the Properties tab in the System Overview. Here, you can directly specify server settings for the log-file change of work processes. These modifications are valid until the system reboots. Use the script element CHANGE_LOGGING in order to trigger a forced log-file change.
To avoid endless reports for events, RemoteTaskManagers, Sync objects, and Schedule objects, their reports are also changed and a new statistical record begins. In this case, only the setting of CHANGE_LOGGING_DAYS is relevant.
CHANGE_LOGGING_MB only works if the setting LOG_TO_DATABASE is set to the value Y. For the Automation Engine, define this setting in the variable UC_SYSTEM_SETTINGS, and for agents, use UC_HOSTCHAR_DEFAULT. CHANGE_LOGGING_DAYS does not depend on this option.
The log files of all work processes are automatically changed if the logging of a work process (WP, DWP, PWP) changes.
The logging of tasks that start on a recurring basis is changed on a daily basis or if the period settings are modified.
CONDITION_CHECK_INTERVAL
The Preconditions tab, which is available in the properties of workflows, can be used to define conditions and statements. These are regularly checked and executed before the tasks start. This process (evaluation cycle) is repeated until the last start time or a final statement has been reached. Use this key to change the time interval. By default, an evaluation takes place every 60 seconds.
DEFAULT_REPORT_SCAN_MEMORY and MAX_REPORT_SCAN_MEMORY
Use DEFAULT_REPORT_SCAN_MEMORY to define the memory size to be requested in order to read reports using a Filter object. The Automation Engine doubles this size if the report to be read is larger. For complex reports, the memory is doubled until the value specified in MAX_REPORT_SCAN_MEMORY has been reached. The task ends with the status FAULT_OTHER if this value is exceeded.
Example:
A report has a size of 10 MB, the default memory is 3 MB, the maximum is 30 MB.
The Automation Engine recognizes that 3 MB is not sufficient to read the report and increases the memory: 3 MB -> 6 MB -> 12 MB. The maximum value for memory has not been exceeded and the report can now be read.
DELETE_CHECKBACK_LIMIT
When you delete an object, the system automatically checks back if this object is also used in other objects. The process as a whole can take a little longer than usual when many objects are deleted simultaneously. Use the key DELETE_CHECKBCK_LIMIT in order to have a query displayed starting with the specified object number, letting you determine whether the usage in other objects should be checked.
DISABLE_USER_HEADER
Job runs also consider Headers and Trailers. These special objects are available in system client 0000 and can be used to call user-defined Include objects. More detailed information is available in the documentation about job includes. If user-defined Include objects should not be used, you can either specify particular platforms or *ALL. Resultantly, these Include objects are not searched, which avoids unnecessary database accesses and improves performance.
Example:
|
Validity |
Value |
|---|---|
|
DISABLE_USER_HEADER |
BS2000,MVS,WINDOWS |
A Java-based work process (JWP) calculates the adaptive expected runtime. If there is no JWP, the ERP cannot be calculated by using this adaptive method.
Use the setting ERT_ADAPTIVE_JWP in order to determine the time in seconds after a system start that the system spends waiting for the adaptive ERT calculations until a JWP is active. After this period of time and when there still is no JWP, the system uses the alternative ERT calculation method which is specified with the setting ERT_ADAPTIVE_FALLBACK_METHOD (UC_CLIENT_SETTINGS).
If the JWP becomes available at a later point, the system will apply the adaptive ERT calculation again.
Note that this setting is only relevant when you intend to calculate the ERT by using the "adaptive" calculation method.
At least one active JWP is needed for the adaptive ERT calculation method.
EXECUTE_ON_EXCEPTION
By default, invalid messages which cause a server process to crash are put into quarantine. Use this key to define that an object should start if such a message is sent. Enter its name as the relevant value.
Note that the object is searched and activated in all clients. System client 0000 is exempted because no objects can be activated in it.
EXTERNAL_CHECK_INTERVAL
This setting determines the frequency at which the status of external dependencies is checked in workflows. The workflow first checks its external dependencies when it starts. The task automatically reports its status when it has ended.
GENERIC_ACTIVITIES_LIMIT
Depending on the specified filter settings, the Activity Window displays the corresponding tasks. If it contains numerous active tasks, performance is affected negatively because refreshing the Activity Window at short intervals is very CPU-intensive. Therefore, you can limit the maximum number of activities to be displayed using the entry GENERIC_ACTIVITIES_LIMIT. A message in the Activity Window's status line indicates that there are more active tasks than displayed. Limit the Activity Window filter so that non-displayed tasks can also be viewed.
GENERIC_AUTO_FORECAST_LIMIT
Auto Forecast filter criteria are very complex. The entry GENERIC_AUTO_FORECAST_LIMIT can be used to limit the maximum number of search results.
GENERIC_SEARCH_LIMIT
In the Explorer, you can search for objects or particular folders. Include the various options in your search. Complex selection criteria can result in a large amount of results and cause long searching times. Therefore, Automic recommends limiting the number of results to be displayed with the entry GENERIC_SEARCH_LIMIT. If the search result is above the value defined here, a message is displayed and only the specified maximum number of results is output.
GENERIC_STATISTICS_LIMIT
Statistical records are automatically created when objects are processed. Selective statistics can be used to search for objects using various options. Complex selection criteria can result in a large amount of results and cause long searching times. To specify a maximum number of records to be displayed, use the entry GENERIC_STATISTICS_LIMIT. A message is displayed if the search result exceeds the value defined here.
GET_PROCESS_LINE_RTRIM
The script functionGET_PROCESS_LINE reads a line of a data sequence (such as a report). Use the entry GET_PROCESS_LINE_RTRIM to determine whether blanks used at the end of the line should be truncated.
LAST_USE
The Header tab of each object contains information about the object's creation and last modification time. It is also possible to display the date of its last use and the total number of executions. The entry in LAST_USE indicates the time in minutes since the last refresh. Executions are not counted if no value or 0 has been specified.
LDAP
LDAP can be used to query information from a directory service such as the Microsoft Active Directory. Users logging in to the AE system can authenticate themselves using this directory service.
LOG_TO_DATABASE
This setting can be used to determine whether the Automation Engine also writes log-file messages to the AE database. Value Y indicates that log messages are saved in the Server object's report. Value N indicates that logging is only performed in the log file. This setting improves the performance of your AE system.
The variable UC_HOSTCHAR_DEFAULT contains a setting of the same name which can be used to specify the agent's log behavior.
MAX_EXPORT_COUNT
During the exporting process, information about the objects highlighted in the Explorer (name, attributes, etc...) is written to a common XML file. To limit the maximum number of objects that can be exported at the same time, use the entry MAX_EXPORT_COUNT. Exceeding this value means that the process has failed. A corresponding error message indicates this.
MAX_IMPORT_SIZE
Use this entry to limit the maximum size of an XML file which should be imported. The import does not take place if the file exceeds the specified value.
MIN_EVENT_INTERVAL
For each event, you can specify a minimum interval (minutes) for its execution in the corresponding Event tab. To define a lower limit, use the entry MIN_EVENT_INTERVAL. The interval specified here is applied if an event contains a value below this limit. AE uses the value specified in the variable UC_JOB_CHECKINTERVAL if 0 is entered here.
Use this key to define the maximum number of server messages to be buffered for further analysis. Only messages which have been sent or received by work processes (PWP, DWP, WP) are affected. These messages are saved in the random access memory (RAM) of the computer on which the Automation Engine is running.
Open the latest messages that have been buffered via the System Overview -> Automation Engine section. Here, select the Workload menu item in a WP's context menu.
MQ_BLOCK_COUNT and MQ_CHECK_TIME
In Oracle databases, the Automation Engine checks the block size of the message queues MQPWP, MQWP, MQDWP, MWRWP, MQOWP and MQCPnnn at the interval specified in MQ_CHECK_TIME . If the block size exceeds the value specified in MQ_BLOCK_COUNT, the Automation Engine reorganizes the message queue, improving the performance of your AE system.
PASSWORD_EXIT
This entry facilitates a password exit. The value to be specified is the name and path of the generated program library.
Example: PASSWORD_EXIT c:\AUTOMIC\pwexit\bin\xuc4pass.dll
PASSWORD_EXIT_PARAM
If parameters need to be assigned, do so using the PASSWORD_EXIT_PARAM key.
PASSWORD_CHANGE
Use this key to define whether the password can be changed.
Example: PASSWORD_CHANGE NO
This entry specifies a time interval during which the server processes try to establish a connection. This affects the connection attempts for a restart or after a lost connection.
REPORT_BLKSIZE and REPORT_TIME
Use these entries to determine the report size in bytes. You can also specify the interval (seconds) at which the report will be refreshed.
RESERVED_API_USERS
Every user who uses the CallAPI needs a free dialog license. These dialog licenses are shared with the users who log in to AE via the UserInterface. The number of dialog licenses specified here is reserved for CallAPI users. In doing so, the CallAPI cannot be blocked due to a lack of free dialog licenses.
Example: "5" is entered in the variable and there are 20 licenses available for the dialog. No further logins would be allowed after the fifteenth login via the UserInterface. It is possible for five additional users to log in to the Automation Engine via the CallAPI. If there are enough available dialog licenses, more users than defined here can use the CallAPI at the same time.
Logging in to system client 0000 is possible even if all dialog licenses are in use. The administrator can always log in to the AE system.
SCR_LOOPCHK_TIME
This setting affects scripts whose generation takes longer than specified here. In such cases, script generation repeatedly pauses for in order to avoid unnecessary Automation Engine loads. Use this method to avoid endless loops.
Use SCR_LOOPCHK_TIME to define the frequency at which the script is interrupted. The subsequent waiting time is always 1 second at the start. This time is doubled after every interruption. The longest waiting time is 128 seconds. After this value has been reached, the waiting time is always 128. It is no longer doubled.
Example for SCR_LOOPCHK_TIME 3:
|
Intervals for Script generation |
|
|---|---|
|
Script starts |
Generation starts |
|
after 3 seconds |
Generation pauses |
|
Waiting time |
Duration: 1 second |
|
Script continues |
Generation continues |
|
after further 3 seconds |
Generation pauses |
|
Waiting time |
Duration: 2 seconds |
|
Script continues |
Generation continues |
|
after further 3 seconds |
Generation pauses |
|
Waiting time |
Duration: 4 seconds |
|
etc. |
|
Script generation always stops every 5 seconds, regardless of the value specified in SCR_LOOPCHK_TIME. Doing so ensures that the script can be canceled without blocking other tasks. A higher value for SCR_LOOPCH_TIME affects the waiting time interval (see above).
SERVER_OPTIONS
This key can be used to handle server settings regarding performance improvements and trace outputs. Its value is composed of a 15-digit string with each digit representing a particular server setting. These values can be read using the script function GET_UC_SETTING.
|
Position |
Character |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1st digit |
S |
Avoids deadlocks especially when starting workflows with DB2. This digit is only relevant for DB2. |
|
2nd digit |
P |
Avoids deadlocks especially when deactivating workflows with DB2. This setting is ignored, the behavior always corresponds to the value "P". This digit is only relevant for DB2. |
|
3rd digit |
S |
With this setting, the statistical records are not checked when a server cold start is performed. This improves the booting performance of large Automation Engine systems (especially in combination with Oracle databases) because in most cases, the statistical records remain unchanged. This is an update statement against the database and using a NULL value column and as far we know in Oracle databases null values are not within the index. This update will set the timestamp4 for all records within AH where we do not have any EH anymore and the timestamp4 is null. In large systems, this simple update could take up to 10 minutes on start-up. To avoid this, it can be turned off. There is no hard and fast definition for a large system. A large system could consist of tens of thousand sof activities, but it depends on many factors such as database speed and IO. |
|
4th digit |
M |
Extends traces so that memory leaks are found more easily. |
|
5th digit |
X |
XML messages (for example, OS messages) can contain invalid characters. With this setting, an additional message and the relevant XML message (memory dump) are written to the server log file. |
|
6th digit |
U |
An additional way to avoid deadlock, especially for DB2. This digit is only relevant for DB2. |
|
7th digit |
G |
Configuration for the restart behavior of tasks. |
|
8th digit |
E |
Avoids DB2 database problems especially when activating file transfers. |
|
9th digit |
D |
If you activate this option, agents are no longer disconnected. Instead, a warning is printed to the log in the frequency of KEEP_ALIVE as long as this connection is inactive. The value KEEP_ALIVE is taken from UC_HOSTCHAR_*. |
|
10th digit |
S or A |
Configuration for report lengths in Sync object reports. S - The Automation Engine does not create Sync object reports.
|
|
11th digit |
Number |
Extended output of time-critical database accesses in the log file. The Automation Engine logs the bind parameters of all time-critical database accesses whose select statements take more seconds than specified in this server option. Any number between 1 and 9 can be specified. Note that regardless of this setting, bind parameters will not be logged in insert statements. When this option is used, 3 is often recommended. This way the bind parameter of all selects that take more than 3 seconds will be logged. Therefore, the Automation Engine logs the BIND VARIABLES for long running SQL statements within the LOG file without the need for a trace. |
|
12th digit |
I |
Setting this option has the effect that no report is written for import processes. |
|
13th digit |
S |
Alternative method for Oracle databases in order to read server messages from the queue. This method is slower than the default method. |
| 14th digit | P |
This option has the effect that the output of the script statement :PRINT is also written to the Automation Engine log if you activate the tasks
Doing so can result in extensive reports and log files. Deactivate this server option in order to increase the performance of your AE system. |
| 15th digit | Y |
Affects the naming of wildcard file transfers from or to z/OS if the source file name includes several wildcard characters. For example: Source is UC4*A.AAA.AA.AAA.A????.A????.A?????? Y - The target file name is correctly built according to the wildcard characters. After the transfer, the file UC4ZZA.AAA.AA.AAA.A1111.A1111.A111111 is given exactly the same name. N - The characters that start with the first wildcard until the last character minus one are ignored. After the transfer, the file UC4ZZA.AAA.AA.AAA.A1111.A1111.A111111 is given the name UC41. Whatever you specify, this option is ignored in the new file transfer protocol. Wildcards are always correctly resolved. |
Activate the particular settings by inserting the respective letters in the relevant positions. The character N is used to deactivate a server option. By default, all Server options are deactivated (NNNNNNNNNNNNNNN).
In the example shown below, options 1, 2, 6 and 8 are activated:
|
Key |
Value |
|---|---|
|
SERVER_OPTIONS |
SPNNNUNENNNNNNN |
If a ServiceManager is used, you can execute its actions directly via the AE system. The relevant commands can either be called directly from the System Overview (Agents / AutomationEngine) or via the script element MODIFY_SYSTEM.
This key can be used to specify the port number or a port area for the automatic search for ServiceManager instances. Doing so is only required if the ServiceManager does not run on the default port 8871.
The system automatically searches for a ServiceManager when the server processes start for the first time. Subsequently, this search must be executed manually using the "Refresh ServiceManager Scan" command in the System Overview. You can also specify the connection settings for the ServiceManager manually in the agent or Server object.
You can specify a port area by separating the start and end port by a comma. This area must not exceed 10 port numbers. Enclose the value in parentheses ( ) in this case.
For example: (8871, 8873)
Use this setting to define the interval at which the display for the blocked workflows for SNMP is refreshed. The default value is 10 seconds.
By default, the creation of Variable objects of the type "SQL - internal" / "SQL - internal SECURE" is deactivated. This is due to security reasons, as the execution of SQL statements on the AE database enables system-wide access to objects and other data. Important data records can also be modified or deleted.
Set SQLVAR_INTERNAL to the value YES in order to create, edit, and use internal SQL variables on a system-wide basis. To do so, a user must have the "Create and modify SQL-Internal variables" privilege.
NO has the effect that the objects cannot be created anymore. The variable type SQLI is no longer listed in the Templates dialog (new object).
The internal SQL variables that are supplied by default in client 0 are not affected by this setting and can always be used.
Databases often supply huge amounts of data. Therefore, you can limit the number of lines to be retrieved by Variable objects with the source SQL and SQLI. Specifying a very high value has the effect that it takes correspondingly longer to resolve Variable objects.
This setting does not have any effect on variables of the types Filelist and Multi.
For performance reasons, log-file changes of Sync objects are performed by block. This means that the log files of a specified number of Sync objects are changed. The log files of the remaining Sync objects are changed in the next blocks.
This setting can be used to determine the number of Sync objects whose logs are to be changed per block. The lower the value, the longer the process will take as a whole. However, a value that is too high can negatively affect the performance of the AutomationEngine.
TRASHBIN_SHOW_MAX
The value that is specified here determines the maximum number of objects to be shown in the Recycle Bin. The current date serves as the basis for this, i.e., the last n objects are visible.
UNREAD_MESSAGES and UNREAD_MESSAGES_BUFFER
The setting here determines the further handling of administrator messages which occur during operation without a user being logged in with the privilege to view them. "N" means that the messages are written to the database without being displayed again. In this case, use the category messages in the System Overview to view these messages at a later point. "Y" indicates that messages are kept and displayed in the Message Window for the next user with a suitable privilege.
Use the UNREAD_MESSAGE_BUFFER to determine the number of unread messages to be kept. The oldest entry will be overwritten once the number of messages is exceeded.
When the Message Window has displayed its unread entries to a user, these are marked as read and removed from the input buffer.
Note that unread messages are lost when:
Messages are always written to the database. Activating this function causes unread entries to be highlighted so that they can be displayed in the Message Window at a later point in time.
You can use this key to determine whether variables can be used in VARA objects, and which ones.
This affects the replacement procedure of variables that are used within SQL statements (VARA types: SQL and SQLI) and OS commands (VARA type: Backend).
The documentation about the dynamic PromptSet dialogs describes the positions where PromptSet variables can be replaced (security level 3).
The following table lists the variables and the security levels at which they are replaced:
| Security level | Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predefined variables (User cannot directly change the value) |
Predefined variables (User can change the value) |
Placeholder for VARA objects | PromptSet variables | |
| 0 | ||||
| 1 |
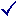
|
|||
| 2 |

|

|
||
| 3 |

|

|

|

|
The security levels of all predefined variables are provided here.
Note for security level 3: You can execute all SQL statements and OS commands that are included in the value to be inserted in the specified Variable object.
A script is used to change the content of the variable VARA2 whose value will be inserted in the SQL statement:
:PUT_VAR VARA2, '*', 'Value; DELETE * FROM x;'
An additional SQL command has been inserted in the SQL variable VARA1 (value replacement) because the content of the Variable object VARA2 has been changed. This was possible although VARA1 has not directly been changed (for example by a user without the corresponding rights) and can also lead to unintended database accesses (in this case: the deletion of data).
The setting VAR_SECURITY_LEVEL has no effect if you access Variable objects of client 0. In this case, they can always be used.
VARIABLE_SERVICE_CHECK_INTERVAL
Dynamic variables can either be used as predefined variables or via script elements in objects. Their values are dynamically retrieved from the data source (database, Variable object or file-system directory) at runtime. If the database variable (source: SQL) runs into an error while resolving the variable because the database is not available or due to incorrect connection or login data, the task switches to a waiting condition ("Waiting for continuation of variable resolving").
Variable resolving can be repeated as soon as the particular error has been cleared (for example, the database name in the connection object has been corrected). The interval at which this attempt is to be repeated is specified by the setting VARIABLE_SERVICE_CHECK_INTERVAL.
Note that you cannot cancel tasks that are in the condition "Waiting for continuation of variable resolving".
VERSIONS_SHOW_MAX
The value that is specified here determines the maximum number of objects to be shown in Version Management. The current date serves as the basis for this, i.e., the last n objects are visible.
WORKLOAD_DEFAULT_FT and WORKLOAD_DEFAULT_JOB
These two settings determine the resources a file transfer or job uses by default. This value can be individually specified in the corresponding objects and overrides the default value specified in the variable.
WP_MIN_NUMBER
Extra server processes (DWPs) are available for messages sent to the database by UserInterfaces. These are special types of work processes (WP). Specify the number of server processes to act as work processes using the entry WP_MIN_NUMBER. The remaining processes can be used as dialog processes (DWP).
Note that the primary work process (PWP) is not included.
Define a node name in the Automation Engines' INI files, as server processes can be distributed among several computers. The minimum number of work processes is valid per "node name". If you use the same "node name" on different computers, this setting is valid for the network.
Your AE system can also run without dialog processes.
XML_ENCODING and XML_ENCODING_CHECK
The XML encoding influences the display of characters in the UserInterface. Use the key XML_ENCODING to specify the encoding to be used for your AE system. The second key affects the verification of imported XML files.
ISO-8859-15 (Latin 9) contains the Euro (€) character and Western-European country-specific special characters. The table below lists additional differences:
| Characters | € | Š | š | Ž | ž | Œ | œ | Ÿ | ¤ | ¦ | ¨ | ´ | ¸ | ¼ | ½ | ¾ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO-8859-15 |
A4 |
A6 |
A8 |
B4 |
B8 |
BC |
BD |
BE |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| ISO-8859-1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
A4 |
A6 |
A8 |
B4 |
B8 |
BC |
BD |
BE |
| WINDOWS-1252 |
80 |
8A |
9A |
8E |
9E |
8C |
9C |
9F |
A4 |
A6 |
A8 |
B4 |
B8 |
BC |
BD |
BE |
OBJECT_ACCESS_CLIENT_ZERO
Setting this key's flag to Y allows users to access system client objects in READ ONLY mode. By using the context menu in a Script object or the UserInterface you can open those objects in READ ONLY mode to check their reports or statistics.
Also see:
UC_CLIENT_SETTINGS
Overview of all the variables in table format
Variable